One-Stage Versus Two-Stage Gastrectomy for Perforated Gastric Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40648977
- PMCID: PMC12251252
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14134603
One-Stage Versus Two-Stage Gastrectomy for Perforated Gastric Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The optimal surgical management of perforated gastric cancer (PGC) in emergency settings remains controversial. Urgent upfront one-stage gastrectomy (1SG) and two-stage gastrectomy (2SG) with damage-control surgery followed by elective gastrectomy have been proposed. The aim of the present systematic review is to compare short- and long-term outcomes between 1SG and 2SG in the treatment of PGC. Methods: A systematic review and individual patient data (IPD) meta-analysis of studies reporting data of patients undergoing 1SG vs. 2SG for PGC was conducted. The time-dependent effects of surgical interventions were assessed using a likelihood ratio test. Hazard function plots were generated via marginal prediction. Results: Ten retrospective series (579 patients) were included. Overall, 482 patients (83%) underwent 1SG, while 97 patients (17%) were treated with 2SG. A trend toward better short-term oncological outcomes and safety profiles for 2SG compared to 1SG was observed. Long-term outcomes were comparable between 1SG and 2SG, and the IPD meta-analysis showed no statistically significant difference between the two approaches in terms of OS or hazard for mortality at all time points. A trend towards a higher hazard for mortality was observed for 1SG in the first 20 months postoperatively. Conclusions: Our analysis suggests that 1SG and 2SG yield comparable short-term outcomes, although 2SG may be associated with a lower medium-term mortality risk. Further research is needed to identify key factors to improve clinical judgments and decision-making in PGC.
Keywords: damage control surgery; gastrectomy; gastric cancer; gastric perforation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
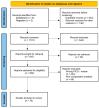
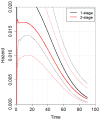
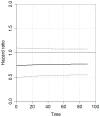
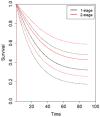
References
-
- Zhang J., Li K., Zhang Z., Zhang G., Zhang S., Zhao Y., Gao Z., Ma H., Xie Y., Han J., et al. Short-and Long-Term Outcomes of One-Stage versus Two-Stage Gastrectomy for Perforated Gastric Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Propensity Score-Matched Study. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2024;22:7. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03283-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

