Spatial Distribution and Post-COVID-19 Health Complications in Older People: A Brazilian Cohort Study
- PMID: 40649148
- PMCID: PMC12250926
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14134775
Spatial Distribution and Post-COVID-19 Health Complications in Older People: A Brazilian Cohort Study
Abstract
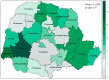
Background/Objectives: In the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 have progressively displayed a range of symptoms linked to protracted COVID during the post-acute phase of illness. Concurrently, in several nations globally, the phenomenon of population aging has been intensifying. In this scenario, the aged population has become both vulnerable and high-risk during the acute phase of COVID-19, and faces significant dangers associated with long-COVID. This study seeks to analyze the incidence and spatial distribution of health complications in older people affected by COVID-19, in the first year of the pandemic (2020), in the State of Paraná, as well as to identify the factors associated with the development of cardiovascular, neurological, respiratory, and metabolic diseases. Method: An observational and retrospective study was carried out in the Brazilian state of Paraná. Participants were randomly selected from two databases. A total of 893 older people (≥60 years) participated in the study 12 months after acute COVID-19 infection. Telephone questionnaires were applied between March and December 2021. The Moran index test, logistic regression, and Poisson models were used to analyze the data. Results: In terms of age, most participants (66%) were between 60 and 69 years old, 25.8% were between 70 and 79 years old, and 8.2% were 80 years old or older. Most participants were female (51.2%), white (98.1%), had a partner (69.8%), and had been hospitalized due to COVID-19 (59.3%). Cardiovascular diseases were the most frequent in the population (39.5%), followed by metabolic diseases (27.3%). The long-term use of medication was associated with the development of metabolic diseases (aOR = 9.8), cardiovascular diseases (aOR = 6.6), and diseases in multiple organic systems (aOR = 3.2); living alone was associated with neurological diseases (aOR = 2.5), and the age group of 80 years or older (aOR = 2.4) was associated with cardiovascular events. The spatial distribution showed that complications in body groups are distributed randomly among the health regions of the state, with no influence from neighboring locations. Conclusions: Post-COVID-19 health complications are more frequent in older adults who have comorbidities and long-term medication use. Therefore, long-term monitoring of these individuals and investment in public policies for rehabilitation and prevention of complications are necessary.
Keywords: Brazil; COVID-19; chronic disease; older people; post-acute COVID-19 syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 30;1(1):CD006207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006207.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36715243 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. 2025. [(accessed on 10 January 2025)]. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=o.
-
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde. Painel Coronavírus. [(accessed on 10 January 2025)];2025 Available online: https://covid.saude.gov.br/
-
- Claessens G., Gach D., van Osch F.H., Verberne D., van den Bergh J.P., van Kampen-van den Boogaart V., Beijers R.J.H.C.G., Schols A.M.W.J., van Balen E. A biopsychosocial analysis of risk factors for persistent physical, cognitive, and psychological symptoms among previously hospitalized post-COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep. 2025;15:14234. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99176-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- FCT-Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P. (UIDB/05704/2020 and UIDP/05704/2020) and by the Scientific Employment Stimulus-Institutional Call - [https://doi.org/10.54499/CEECINST/00051/2018/CP1566/CT0012, accessed on 6 May 2025]/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- grant number: 001/2023/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous