The Role of C-Reactive Protein in Acute Myocardial Infarction: Unmasking Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Insights
- PMID: 40649166
- PMCID: PMC12250735
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14134795
The Role of C-Reactive Protein in Acute Myocardial Infarction: Unmasking Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Insights
Abstract
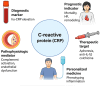
C-reactive protein (CRP) has emerged as a valuable biomarker in acute myocardial infarction (AMI), offering multiple insights into diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic strategies. In the diagnostic domain, elevated CRP levels serve as an early indicator of AMI, aiding in prompt identification and initiation of treatment. Prognostically, CRP is a strong predictor of adverse outcomes post-AMI, correlating with increased mortality and cardiovascular events. Beyond its diagnostic and prognostic roles, CRP also exposes therapeutic avenues in AMI management. Targeting CRP through pharmacological interventions has shown promise in reducing inflammatory responses, thereby mitigating myocardial damage and improving clinical outcomes. However, CRP's low specificity, influenced by elevation in non-cardiac conditions, remains a clinical limitation that warrants consideration. This review comprehensively examines the evolving role of CRP in AMI, exploring its diagnostic accuracy, prognostic significance, and potential as a therapeutic target. The understanding of the complex role of CRP in AMI provides clinicians with valuable tools for risk stratification, treatment optimization, and personalized patient care in the acute setting.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; acute myocardial infarction; biomarkers; cardiovascular risk; diagnosis; immune response; inflammation; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ong S.-B., Hernández-Reséndiz S., Crespo-Avilan G.E., Mukhametshina R.T., Kwek X.-Y., Cabrera-Fuentes H.A., Hausenloy D.J. Inflammation Following Acute Myocardial Infarction: Multiple Players, Dynamic Roles, and Novel Therapeutic Opportunities. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018;186:73–87. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous