Anticancer Quinolinol Small Molecules Target Multiple Pathways to Promote Cell Death and Eliminate Melanoma Cells Resistant to BRAF Inhibitors
- PMID: 40649216
- PMCID: PMC12251381
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30132696
Anticancer Quinolinol Small Molecules Target Multiple Pathways to Promote Cell Death and Eliminate Melanoma Cells Resistant to BRAF Inhibitors
Abstract
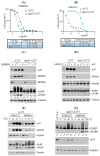
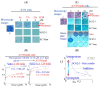
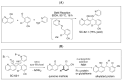
Small molecule inhibitors that target the E3 ligase activity of MDM2-MDM4 have been explored to inhibit the oncogenic activity of MDM2-MDM4 complex. MMRi62 is a small molecule that was identified using an MDM2-MDM4 E3 ligase-based high throughput screen and a cell-death-based secondary screen. Our previous studies showed that MMRi62 promotes MDM4 degradation in cells and induces p53-independent apoptosis in cancer cells. However, MMRi62 activity in solid tumor cells such as melanoma cells, especially in BRAF inhibitor resistant melanoma cells, have not been explored. Although its promotion of MDM4 degradation is clear, the direct MMRi62 targets in cells are unknown. In this report, we show that MMRi62 is a much more potent p53-independent apoptosis inducer than conventional MDM2 inhibitors in melanoma cells. A brief structure-activity study led to development of SC-62-1 with improved activity. SC-62-1 potently inhibits and eliminates clonogenic growth of melanoma cells that acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors. We developed a pair of active and inactive SC-62-1 probes and profiled the cellular targets of SC-62-1 using a chemical biology approach coupled with IonStar/nano-LC/MS analysis. We found that SC-62-1 covalently binds to more than 15 hundred proteins in cells. Pathways analysis showed that SC-62-1 significantly altered several pathways including carbon metabolism, RNA metabolism, amino acid metabolism, translation and cellular response to stress. This study provides mechanistic insights into the mechanisms of action for MMRi62-like quinolinols. This study also suggests multi-targeting compounds like SC-62-1 might be useful for overcoming resistance to BRAF inhibitors for improved melanoma treatment.
Keywords: E3 ligase; MDM2-MDM4; MMRi62; cell death; chemical robe; quinolinol; targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
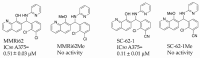

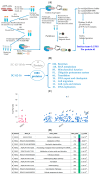
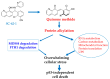
Similar articles
-
BRAF inhibitors in Melanoma: Structural Insights, Therapeutic Resistance, and Biological Evaluation of Quinazoline Derivatives.Eur J Med Chem. 2025 Oct 15;296:117866. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.117866. Epub 2025 Jun 11. Eur J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40541114 Review.
-
Small-molecule MMRi36 induces apoptosis in p53-mutant lymphomas by targeting MDM2/MDM4/XIAP for degradation.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 23;14:1462231. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1462231. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39763603 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting mitochondrial dysfunction to overcome BRAF inhibitor resistance in advanced melanoma: the role of disulfiram as a copper ionophore.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):482. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07766-y. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40592836 Free PMC article.
-
A structure-based virtual screening identifies a novel MDM2 antagonist in the activation of the p53 signaling and inhibition of tumor growth.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Mar;46(3):740-750. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01394-6. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39384887
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

