Degradation of Folic Acid in the Composition of a Conjugate with Polyvinylpyrrolidone and Fullerene C60 Under UV and E-Beam Irradiation
- PMID: 40649237
- PMCID: PMC12251273
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30132718
Degradation of Folic Acid in the Composition of a Conjugate with Polyvinylpyrrolidone and Fullerene C60 Under UV and E-Beam Irradiation
Abstract
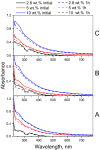
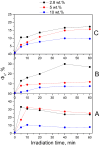
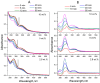
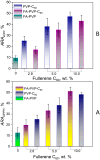
Folic acid (FA) is used as a targeting ligand for targeted drug delivery to tumor cells, some types of which overexpress folate receptors on their surface. However, while the preparation of conjugates containing FA may comprise a multi-step process, FA presents low photostability under UV irradiation. In addition, FA undergoes radiolysis under the action of ionizing radiation, which is utilized for drug sterilization. In this study, we investigate the stability of FA in a conjugate (FA-PVP-C60) with fullerene C60 and polyvinylpyrrolidone under the action of UV (205-400 nm) and electron irradiation (doses from 2 to 8 kGy) at different pH (4.5, 7.2, 10.7). The degradation of FA is studied using fluorescence and UV-Vis spectroscopy. It is found that the fullerene C60 in the FA-PVP-C60 conjugate suppresses the degradation of FA during both photolysis and radiolysis, which is confirmed by the decrease in the quantum yield of fluorescence and the radiation chemical yield of FA destruction accompanied by increasing fullerene content in the conjugate (from 2.8 to 10 wt.%).
Keywords: UV irradiation; folic acid; fullerene; photodegradation; radiation chemical yield; radiolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Dada S.N., Babanyinah G.K., Tetteh M.T., Palau V.E., Walls Z.F., Krishnan K., Croft Z., Khan A.U., Liu G., Wiese T.E., et al. Covalent and Noncovalent Loading of Doxorubicin by Folic Acid-Carbon Dot Nanoparticles for Cancer Theranostics. ACS Omega. 2022;7:23322–23331. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01482. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

