Synthesis of Novel 7-Phenyl-2,3-Dihydropyrrolo[2,1- b]Quinazolin-9(1 H)-ones as Cholinesterase Inhibitors Targeting Alzheimer's Disease Through Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction
- PMID: 40649306
- PMCID: PMC12250785
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30132791
Synthesis of Novel 7-Phenyl-2,3-Dihydropyrrolo[2,1- b]Quinazolin-9(1 H)-ones as Cholinesterase Inhibitors Targeting Alzheimer's Disease Through Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction
Abstract
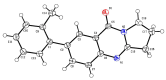
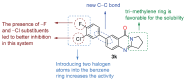
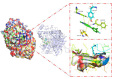
An important field of research in medicinal and organic chemistry involves halogen-containing heterocyclic synthones, which form the backbone of more complex organic compounds. This study aimed to design and synthesize 28 novel derivatives of 7-aryl-2,3-dihydropyrrolo[2,1-b]quinazolin-9(1H)-one. The derivatives were created from 7-bromoquinoline intermediates to evaluate their potential as cholinesterase inhibitors for treating neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. The conditions for the Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction were optimized to improve yield and purity. The derivatives were evaluated for their anticholinesterase activity using Ellman's method, revealing that it most effectively inhibited cholinesterase within the micromolar range. 7-(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydropyrrolo[2,1-b]quinazolin-9(1H)-one derivative exhibited the highest inhibitory potency, with an IC50 value of 6.084 ± 0.26 μM. Additionally, molecular dynamics simulations provided insight into how this lead compound interacts with the enzyme, suggesting its potential as a drug candidate for Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase (AChE); Alzheimer’s disease; Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE); Pd catalyst; Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling; carbon–carbon bond (C-C); deoxyvasicinone; mackinazolinone; quinazoline.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
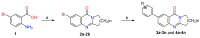




Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of caffeic acid-based novel multifunctional molecules for the management of Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Med Chem. 2025 Oct 15;296:117831. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.117831. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Eur J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40578253
-
Exploring Novel Quinoline-1,3,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives for Alzheimer's Disease: Their Design, Synthesis, and In-Vitro and In-Silico Investigations.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(21):4259-4283. doi: 10.2174/0109298673333159240815061359. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39206477
-
Novel Purine-Based Natural Products as Inhibitors of Cholinesterases and Monoamine Oxidases Presenting Potential Multitarget Therapeutics Tackling Alzheimer's Disease.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025 Jul;358(7):e70035. doi: 10.1002/ardp.70035. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025. PMID: 40629981
-
Physostigmine for Alzheimer's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;2001(2):CD001499. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001499. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. PMID: 11405996 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Jan 25;2006(1):CD005593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005593. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. PMID: 16437532 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pyrrolopyrimidines: Design, Synthesis and Antitumor Properties of Novel Tricyclic Pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyrimidine Derivatives.Molecules. 2025 Jul 10;30(14):2917. doi: 10.3390/molecules30142917. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40733183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rowinska-Zyrek M., Salerno M., Kozlowski H. Neurodegenerative diseases—Understanding their molecular bases and progress in the development of potential treatments. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015;284:298–312. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.03.026. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

