Increasing Life Expectancy with Plant Polyphenols: Lessons from the Mediterranean and Japanese Diets
- PMID: 40649401
- PMCID: PMC12251304
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30132888
Increasing Life Expectancy with Plant Polyphenols: Lessons from the Mediterranean and Japanese Diets
Abstract
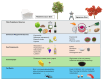
Plant polyphenols have emerged as potent bioactive molecules that can modulate key cellular pathways associated with aging and chronic disorders. The Mediterranean diet and the traditional Japanese style of life are rich in polyphenol-containing foods and beverages, and epidemiological evidence links these dietary patterns to increased longevity and reduced morbidity. This narrative review examines the chemical description of plant polyphenols, their mechanisms of action, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hormetic effects, and how supplementation or a diet rich in these compounds may provide further life extension. We discuss the major classes of polyphenols present in the Mediterranean dietary pattern (e.g., resveratrol and hydroxytyrosol) and in the Japanese diet (e.g., epigallocatechin gallate and soy isoflavones), comparing their biological behaviors and cooperative effects on metabolic, cardiovascular, and neurodegenerative conditions. We also examine a few preclinical and clinical studies that explain the beneficial impact of these chemicals on aging-associated biomarkers. Furthermore, both dietary habits are characterized by low consumption of processed foods and sugary carbonated drinks and reduced utilization of deep-frying with linoleic acid-rich oils, a practice that reduces the formation of harmful lipid peroxidation products, notably 4-hydroxynonenal, known to be implicated in accelerating the aging process. The Mediterranean dietary pattern is also characterized by a low/moderate daily consumption of wine, mainly red wine. This work debates emerging evidence addressing issues of bioavailability, dosage optimization, and formulation technologies for polyphenol supplementation, also comparing differences and similarities with the vegan and vegetarian diets. We also explore how these chemicals could modulate epigenetic modifications that affect gene expression patterns pertinent to health and aging. In conclusion, we aim to show a consolidated framework for the comprehension of how plant polyphenols could be utilized in nutritional strategies for potentiating life expectancy while stimulating further research on nutraceutical development.
Keywords: Japanese diet; aging; antioxidants; longevity; mediterranean diet; nutraceuticals; plant polyphenols; vegan diet; vegetarian diet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sharifi-Rad M., Anil Kumar N.V., Zucca P., Varoni E.M., Dini L., Panzarini E., Rajkovic J., Tsouh Fokou P.V., Azzini E., Peluso I., et al. Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020;11:694. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00694. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Petrella C., Di Certo M.G., Gabanella F., Barbato C., Ceci F.M., Greco A., Ralli M., Polimeni A., Angeloni A., Severini1 C., et al. Mediterranean Diet, Brain and Muscle: Olive Polyphenols and Resveratrol Protection in Neurodegenerative and Neuromuscular Disorders. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021;28:7595–7613. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210504113445. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ungvari A., Nyúl-Tóth Á., Patai R., Csik B., Gulej R., Nagy D., Shanmugarama S., Benyó Z., Kiss T., Ungvari Z., et al. Cerebromicrovascular senescence in vascular cognitive impairment: Does accelerated microvascular aging accompany atherosclerosis? GeroScience. 2025 doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01621-w. ahead of print . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

