Assessment of CA4+ Impact on Mechanical Properties of Articular Cartilage
- PMID: 40649430
- PMCID: PMC12250616
- DOI: 10.3390/ma18132943
Assessment of CA4+ Impact on Mechanical Properties of Articular Cartilage
Abstract
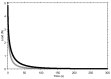
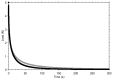
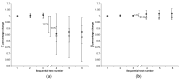
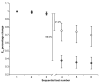
X-ray imaging of articular cartilage could be a breakthrough for the early diagnosis of tissue degeneration. This approach relies on radiopaque contrast agents to enhance the visualization of soft tissues. The potential impact of contrast agents on the mechanical response of articular cartilage should be considered in the frame of both clinical and research applications. Attention has been drawn to a solution containing molecules with six iodine atoms and four positive charges (CA4+), which has been shown to improve the X-ray visibility of articular cartilage. This study aimed to determine the effects of a CA4+ solution on tissues' mechanical properties. An experimental pipeline based on indentation tests was applied to paired samples of articular cartilage before and after the immersion in either CA4+ or phosphate-buffered saline solution, maintained at a temperature of 22 ± 2 °C, for 22 h to determine the differences in instantaneous, viscous, and equilibrium responses between the articular cartilage of the two groups. The 22 h immersion of articular cartilage in either CA4+ or phosphate-buffered saline solution had a significant detrimental effect on the overall response, including the instantaneous, viscous, and equilibrium responses, of the articular cartilage. However, this detrimental effect was greater with exposure to the CA4+ solution. Specifically, the articular cartilage was found to be less stiff in both the instantaneous response (approximately -25%) and the equilibrium response (approximately -38%). The softening effect could be attributable to an alteration of the interaction between the proteoglycans of articular cartilage, induced by the positive charges within the CA4+ contrast agent. Further investigations are needed to elucidate whether this hypothesized mechanism is reversible.
Keywords: X-ray imaging; articular cartilage; cartilage degeneration; characterization of materials; contrast agent; contrast-enhanced imaging; early diagnosis; indentation; mechanical properties; soft tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of this manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

