Thin-Film Encapsulation for OLEDs and Its Advances: Toward Engineering
- PMID: 40649664
- PMCID: PMC12251312
- DOI: 10.3390/ma18133175
Thin-Film Encapsulation for OLEDs and Its Advances: Toward Engineering
Abstract
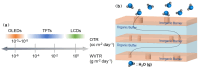
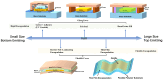
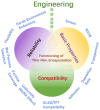
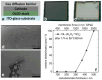
Thin-film encapsulation has been a critical method to realize small-size OLED displays. However, the manufacturing of large-size flexible OLED is still in the preparatory phase prior to commercialization, which entails more rigorous demands for reliability and flexibility with regard to thin-film encapsulation. This review, from the perspective of engineering for mass production, addresses the development of thin-film encapsulation and its three core properties for comprehensive validation while engineering, including basic properties, reliability, and compatibility. Moreover, considering the prospective evolution of display products, the review on novel thin-film encapsulation was conducted to evaluate the potential engineering value for thinning, ultra-flexibility, multifunctionality, novel equipment, and emerging technology. It is anticipated that some of the aforementioned technologies may prove to be of significant engineering value. It is therefore hoped that by comprehensive engineering verification, the commercial application of novel thin-film encapsulation can be promoted and the competitiveness of OLED products can be effectively enhanced.
Keywords: engineering; large-size OLEDs; multifunctionality; thin-film encapsulation; thinning; ultra-flexibility.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Songju Li, Zhuo Gao, Xiaolin Yan, Dong Fu and Xianwen Sun were employed by the company Guangdong Juhua Printed Display Technology Co., Ltd. Author Min Li was employed by the company Guangzhou New Vision Optoelectronic Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
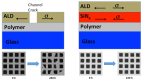
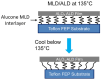
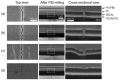
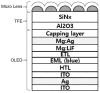


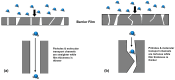
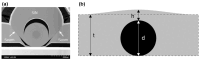
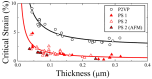




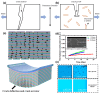
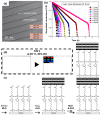






References
-
- Adachi C., Nagai K., Tamoto N. Molecular design of hole transport materials for obtaining high durability in organic electroluminescent diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995;66:2679–2681. doi: 10.1063/1.113123. - DOI
-
- Xu R.-P., Li Y.-Q., Tang J.-X. Recent advances in flexible organic light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2016;4:9116–9142. doi: 10.1039/C6TC03230C. - DOI
-
- He P., Lan L., Deng C., Wang J., Peng J., Cao Y. Highly efficient and stable hybrid quantum-dot light-emitting field-effect transistors. Mater. Horiz. 2020;7:2439–2449. doi: 10.1039/D0MH00951B. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 2024YFF1504501, 2022YFB3603805, 2021YFB3600800, 2021YFB3602704/National Key R&D Program of China
- 62474070, 62074059/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024ZD0604100/Advanced Materials-National Science and Technology Major Project
- None/TCL Science and Technology Innovation Fund
- Skllmd-2024-04/Autonomous Project of State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

