Investigation of In Vitro and In Silico Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Carthamus caeruleus L. Root Juice
- PMID: 40649743
- PMCID: PMC12249700
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26135965
Investigation of In Vitro and In Silico Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Carthamus caeruleus L. Root Juice
Abstract
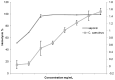
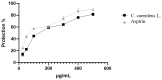
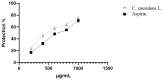
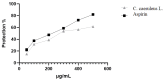
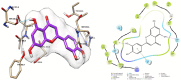
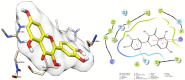
This study aimed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory properties of Carthamus caeruleus L. root juice (CRJ), which is used in the traditional medicine of Algeria. The product was characterized by colorimetric assays (total polyphenols, flavonoids, and tannins) and by RP-HPLC-DAD analysis. Experiments were conducted in vitro to assess the ability of CRJ to stabilize human erythrocyte membranes under various stress conditions and inhibit albumin denaturation, a process linked to inflammation. An in silico study was also performed to investigate the inhibitory effects on cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and assess the phenolic constituents with the highest activity. Moderate levels of polyphenols, flavonoids, and tannins were assessed; among these, 22 compounds were identified via chromatographic analysis. While present at low concentrations, some of these compounds, including myricetin, luteolin, and quercetin, are known to exhibit bioactivity at micromolar levels. CRJ provided erythrocyte membranes with notable protection against disruption caused by hypotonic NaCl solutions (protection levels of 90.51%, 87.46%, and 76.87% at NaCl concentrations of 0.7%, 0.5%, and 0.3%, respectively), heat stress (81.54%), and oxidative damage from HClO (75.43%). Additionally, a protection of 61.5% was observed against albumin denaturation. Docking analysis indicated favorable COX-2 binding for myricetin, luteolin, and quercetin. In conclusion, the root juice derived from C. caeruleus demonstrated potential anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in silico. However, further studies, including in vivo investigations, are necessary to confirm efficacy and fully elucidate the mechanisms of action.
Keywords: COX-2 inhibition; Carthamus caeruleus; RP-HPLC; anti-inflammatory; erythrocyte stabilization; molecular docking; root juice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- GBD Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

