A Liposomal Strategy for Dual-Action Therapy in Sarcopenia: Co-Delivery of Caffeine and HAMA
- PMID: 40649810
- PMCID: PMC12249999
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136031
A Liposomal Strategy for Dual-Action Therapy in Sarcopenia: Co-Delivery of Caffeine and HAMA
Abstract
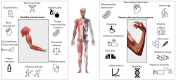
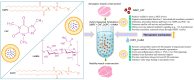
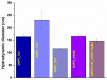
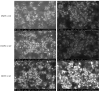
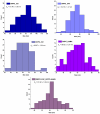
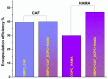
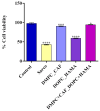
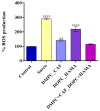
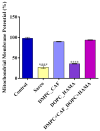
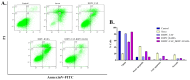
The biological complexity of sarcopenia presents a major challenge for therapeutic intervention due to the wide range of degenerative changes it induces in skeletal muscle. This study demonstrates the potential of liposomal controlled release systems to address these challenges by combining two bioactive agents with complementary actions: caffeine (CAF), encapsulated in DMPC-based liposomes, and hyaluronic acid methacrylate (HAMA), encapsulated in DOPC-based liposomes. A hybrid system was also developed to deliver both substances simultaneously, aiming to restore tissue function through combined metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative effects. The liposomes exhibited nanoscale dimensions, spherical morphology, and intact membrane structure, as confirmed by electron microscopy. DLS analysis indicated good colloidal stability and monodisperse size distribution across all formulations, with improved stability observed in the hybrid system. Drug release studies showed a time-dependent profile, with HAMA releasing rapidly and CAF releasing gradually, supporting a dual-action therapeutic approach tailored to the multifactorial pathology of sarcopenia. The biological assays, performed in an established in vitro sarcopenia model, revealed the potential of liposomes co-delivering caffeine and HAMA to mitigate oxidative stress, preserve mitochondrial function, and reduce apoptosis in H2O2-damaged myotubes.
Keywords: caffeine; hyaluronic acid methacrylate; liposomal hybrid drug delivery system; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

