Targeted Therapy for Complex Lymphatic Anomalies in Patients with Noonan Syndrome and Related Disorders
- PMID: 40649904
- PMCID: PMC12250309
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136126
Targeted Therapy for Complex Lymphatic Anomalies in Patients with Noonan Syndrome and Related Disorders
Abstract
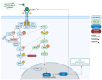
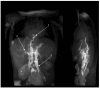
Recent diagnostic advances reveal that lymphatic disease in Noonan syndrome (NS) and other NS-like RASopathies often stems from central conducting lymphatic anomalies (CCLAs). The RAS/MAPK-ERK pathway plays a central role in lymphangiogenesis. Targeting this pathway with MEK-inhibitor trametinib has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for managing CCLAs in patients with NS-like RASopathies. This case series assessed the clinical outcomes of trametinib therapy in eight patients with NS-like RASopathies and CCLA, each offering unique insights into the therapeutic efficacy of MEK inhibition. In infants, a lower dose of 0.01 mg/kg/day and earlier discontinuation of trametinib therapy effectively alleviated the symptoms of congenital chylothorax and rescued the lymphatic phenotype, compared to similar published cases. Moreover, four patients aged >11 y showed a slower response and did not achieve complete symptomatic recovery. In conclusion, it is advised to consider trametinib therapy for patients with severe, therapy-refractory CCLA in patients with NS-like RASopathies. However, individual responses to trametinib therapy may vary, with some patients demonstrating more favorable outcomes than others. Further investigation into potential enhancers and suppressors of the lymphatic phenotype is necessary for more accurate treatment predictions. While these factors are likely genetic, we cannot rule out other intrinsic or physiological factors.
Keywords: CCLA; Noonan syndrome; RASopathies; genetics; lymphatic anomaly; targeted therapy; trametinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular targeted treatment in infants with central conducting lymphatic anomalies.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 Aug 21;184(9):567. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06376-2. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40835771 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting cardiomyopathies associated with RASopathies: the role of mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors and therapeutic challenges.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2025 Aug 1;35(6):173-182. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000569. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40460044 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic interventions for treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS/TEN overlap syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 11;3(3):CD013130. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013130.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35274741 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Molecular targeted treatment in infants with central conducting lymphatic anomalies.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 Aug 21;184(9):567. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06376-2. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40835771 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

