Applications of Spatial Transcriptomics in Veterinary Medicine: A Scoping Review of Research, Diagnostics, and Treatment Strategies
- PMID: 40649940
- PMCID: PMC12249720
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136163
Applications of Spatial Transcriptomics in Veterinary Medicine: A Scoping Review of Research, Diagnostics, and Treatment Strategies
Abstract
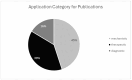
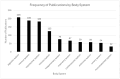
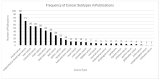
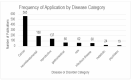
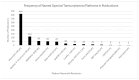
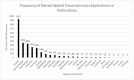
Spatial transcriptomics is an emerging technology that maps gene expression within tissue architecture. Its expanding use in medicine and veterinary science supports research, precision diagnostics, biomarker discovery, and development of targeted treatment strategies. While spatial transcriptomics applications in human health are well-documented with significant publication diversity and volume, published applications in veterinary medicine remain limited. A comprehensive search of PubMed was conducted, focusing on studies published from 2016 to early 2025 that employed spatial transcriptomics in the context of disease research, diagnosis, or treatment in human or animal health. The review followed the Arksey and O'Malley framework and adhered to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines. A total of 1398 studies met the inclusion criteria. The studies highlighted emerging trends of comparative research with animal model use for human health research. Commonly used spatial transcriptomics platforms included 10× Visium, Slide-seq, Nanostring (GeoMx, CosMX), and multiplexed error-robust fluorescence in situ hybridization (MERFISH). Key gaps in publications include limited veterinary representation, interspecies comparisons, standardized methods, public data use, and therapeutic studies, alongside biases in disease, species, organ, and geography. This review presents the current landscape of spatial transcriptomics publications for human and animal research and medicine, providing comprehensive data and highlighting underrepresented research areas and gaps for future consideration.
Keywords: spatial; transcriptomics; veterinary medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

