Exosomes Derived from Induced and Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Senescence-like Features and Migration in Cancer Cells
- PMID: 40649957
- PMCID: PMC12249808
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136178
Exosomes Derived from Induced and Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Senescence-like Features and Migration in Cancer Cells
Abstract
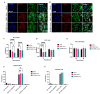
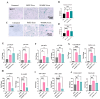
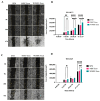
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-Exos) play a key role in tissue repair, immune regulation, and cancer biology. Due to limitations in MSC expansion and source variability, interest has shifted to induced pluripotent stem cell-derived MSCs (iMSCs) as a promising alternative. This study compares effects of exosomes derived from iMSCs (iMSC-Exos) and Wharton's jelly MSCs (WJMSC-Exos) on MCF7 and A549 cancer cells. Both types of exosomes reduced MCF7 proliferation and induced a senescence-like state, rather than apoptosis, although the antiproliferative effect was transient in A549 cells. Notably, WJMSC-Exos promoted migration in both MCF7 and A549, whereas iMSC-Exos did not exhibit this effect. Overall, WJMSC-Exos had a more robust impact on cancer cell proliferation and migration. These findings highlight the diverse effects of exosomes on cancer and the development of a senescence-like state as an important response to Exos exposure. Moreover, these findings invite for more careful evaluation of the therapeutic role of iMSC-derived Exos.
Keywords: Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells (WJMSCs); cancer; cell-free therapy; exosomes; induced mesenchymal stem cells (iMSCs); senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of exosomes derived from induced and human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells on human cancer cells.J Biosci. 2025;50:43. J Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40501094
-
Comparative Efficacy of Exosomes Derived from Different Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sources in Osteoarthritis Models: An In Vitro and Ex Vivo Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 6;26(12):5447. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125447. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564912 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer of miR-126.Acta Biomater. 2020 Feb;103:196-212. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.12.020. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 31857259
-
"Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-exosomes) in hematology: From mechanisms to clinical breakthroughs".Cell Immunol. 2025 Aug;414:104986. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2025.104986. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Cell Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40499318 Review.
-
Cutting-edge insights into liver fibrosis: advanced therapeutic strategies and future perspectives using engineered mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Aug;15(8):2608-2623. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01784-7. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39853531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

