The Production of Recombinant Azurin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Ability to Induce Apoptosis in Various Breast Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 40649966
- PMCID: PMC12250392
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136188
The Production of Recombinant Azurin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Ability to Induce Apoptosis in Various Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
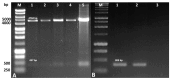
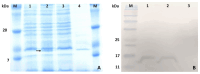
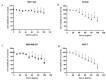
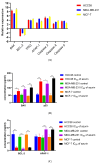
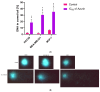
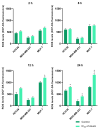
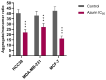
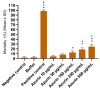
Azurin is a copper-containing redox protein naturally produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which has shown promising activity against human cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. The present study describes the design of a recombinant vector, pT7-MAT-Tag-2-Azu, for azurin production in E. coli cells. The cytotoxic effects of purified azurin were tested on three breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, and HCC38) and a normal breast epithelial cell line (MCF10A) using the MTT assay. The results showed cytotoxicity against cancer cell lines with minimal effects on normal cells. Further analysis showed that azurin induced apoptosis through mitochondrial pathways, as evidenced by increased expression of apoptosis-related genes (Bax, TP53, Apaf-1, caspase-3, -8, -9) and their corresponding proteins, elevated levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and DNA damage, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), or brine shrimp lethality assay. Furthermore, in silico molecular docking, simulations predicted a stable, electrostatically driven interaction between azurin and the p53 protein, providing a structural basis for its mechanism of action. These findings suggest that recombinant azurin may serve as a potential therapeutic agent for breast cancer after further multifaceted research.
Keywords: anticancer; apoptosis; azurin; breast cancer; recombinant proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

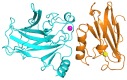
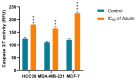
References
-
- Maiorella B., Inlow D., Shauger A., Harano D. Large-Scale Insect Cell-Culture for Recombinant Protein Production. Bio/Technol. 1988;6:1406–1410. doi: 10.1038/nbt1288-1406. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

