Enhancement of 3-MA in Paclitaxel Treatment of MDA-MB-231 Tumor-Bearing Nude Mice and Its Mechanisms
- PMID: 40649969
- PMCID: PMC12249906
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136191
Enhancement of 3-MA in Paclitaxel Treatment of MDA-MB-231 Tumor-Bearing Nude Mice and Its Mechanisms
Abstract
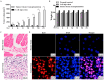
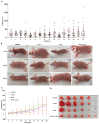
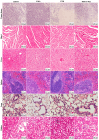
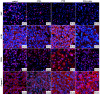
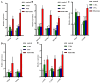
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) poses significant challenges due to its high aggressiveness, poor prognosis, and the lack of effective targeted therapies. Paclitaxel (PTX) is a chemotherapeutic agent commonly used in the treatment of TNBC; however, its efficacy is often compromised by drug resistance mediated by autophagy. This study investigated the synergistic effects of the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA) and PTX in a TNBC nude mouse model. Monitoring tumor volume and employing HE staining, immunofluorescence, and transmission electron microscopy revealed that PTX monotherapy induced tumor autophagy, characterized by the accumulation of LC3B/VPS34 proteins and an increase in autophagosomes. However, the co-administration of 3-MA reversed this process, significantly decreasing the tumor growth rate. Immunofluorescence and qPCR demonstrated that the combination group had fewer Ki-67-positive cells and more Caspase-3-positive cells, along with upregulated expression of autophagy-related genes and Caspase-family apoptosis genes. Consequently, this study suggests that inhibiting autophagy with 3-MA disrupts the autophagy-mediated protective mechanism of tumor cells, promoting the activation of apoptotic signals and enhancing the antitumor activity of PTX. These findings may offer new molecular mechanistic insights and potential therapeutic strategies for overcoming PTX resistance in TNBC.
Keywords: 3-MA; MDA-MB-231; autophagy; paclitaxel; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmad A. Breast Cancer Statistics: Recent Trends. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019;1152:1–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

