Estradiol Prevents Amyloid Beta-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurotoxicity in Alzheimer's Disease via AMPK-Dependent Suppression of NF-κB Signaling
- PMID: 40649980
- PMCID: PMC12249544
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136203
Estradiol Prevents Amyloid Beta-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurotoxicity in Alzheimer's Disease via AMPK-Dependent Suppression of NF-κB Signaling
Abstract
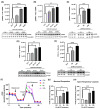
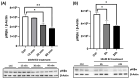
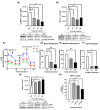
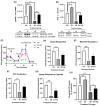
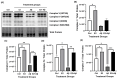
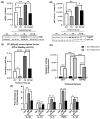
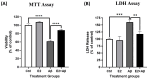
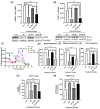
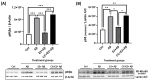
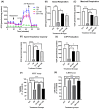
Alzheimer's disease (AD), the most common form of dementia, is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by memory loss and cognitive decline. In addition to its two major pathological hallmarks, extracellular amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), recent evidence highlights the critical roles of mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation in disease progression. Aβ impairs mitochondrial function, which, in part, can subsequently trigger inflammatory cascades, creating a vicious cycle of neuronal damage. Estrogen receptors (ERs) are widely expressed throughout the brain, and the sex hormone 17β-estradiol (E2) exerts neuroprotection through both anti-inflammatory and mitochondrial mechanisms. While E2 exhibits neuroprotective properties, its mechanisms against Aβ toxicity remain incompletely understood. In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective effects of E2 against Aβ-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation in primary cortical neurons, with a particular focus on the role of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). We found that E2 treatment significantly increased phosphorylated AMPK and upregulated the expression of mitochondrial biogenesis regulator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 α (PGC-1α), leading to improved mitochondrial respiration. In contrast, Aβ suppressed AMPK and PGC-1α signaling, impaired mitochondrial function, activated the pro-inflammatory nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), and reduced neuronal viability. E2 pretreatment also rescued Aβ-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, suppressed NF-κB activation, and, importantly, prevented the decline in neuronal viability. However, the pharmacological inhibition of AMPK using Compound C (CC) abolished these protective effects, resulting in mitochondrial collapse, elevated inflammation, and cell death, highlighting AMPK's critical role in mediating E2's actions. Interestingly, while NF-κB inhibition using BAY 11-7082 partially restored mitochondrial respiration, it failed to prevent Aβ-induced cytotoxicity, suggesting that E2's full neuroprotective effects rely on broader AMPK-dependent mechanisms beyond NF-κB suppression alone. Together, these findings establish AMPK as a key mediator of E2's protective effects against Aβ-driven mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation, providing new insights into estrogen-based therapeutic strategies for AD.
Keywords: AMPK; Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid-β; NF-κB; estradiol; mitochondria; neuroinflammation; neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
P.M., E.K.E., and B.C.A. declare that they have no competing interests. P.F. is a cofounder and shareholder in a small biotech company, WinSanTor Inc., that is developing antimuscarinic drugs for the treatment of peripheral neuropathy.
Figures
References
-
- Gallardo G., Holtzman D.M. Amyloid-β and Tau at the Crossroads of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019;1184:187–203. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

