Therapeutic Prospects of αv Integrins Inhibition in Fibrotic Lung Diseases and Carcinogenesis
- PMID: 40649983
- PMCID: PMC12249868
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136202
Therapeutic Prospects of αv Integrins Inhibition in Fibrotic Lung Diseases and Carcinogenesis
Abstract
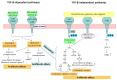
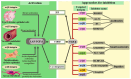
The uncontrolled fibrosis of lung tissue can lead to premature death in patients suffering from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), and it complicates the course of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and emphysema. It is also a risk factor for developing lung cancer. Antifibrotic drugs, such as nantedanib and pirfenidone, are able to slow down the progression of pulmonary fibrosis, but more effective treatment is still needed to reverse it. Studies on the pathogenesis of tissue fibrosis have demonstrated that integrins play a crucial role affecting the development of pulmonary fibrosis, for example, by activating transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). Taking the above into consideration, targeting specific integrins could offer promising opportunities for managing fibroplastic changes in lung tissue. Integrins are a type of transmembrane molecule that mediate interactions between cells and extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules. This review discusses the role of integrins in the pathogeneses of respiratory diseases and carcinogenesis, as well as presents promising approaches to the drug therapy of pulmonary fibrosis of various etiologies based on integrin inhibition.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; lung cancer; αv integrin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Murărescu E.D., Mitrofan E.C., Mihailovici M.S. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a new concept. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2007;48:207–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

