Tuning the Gel Network Structure and Rheology of Acid-Induced Casein Gels via Thiol Blocking
- PMID: 40649984
- PMCID: PMC12249982
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136206
Tuning the Gel Network Structure and Rheology of Acid-Induced Casein Gels via Thiol Blocking
Abstract
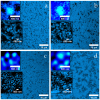
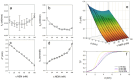
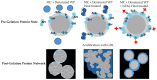
This study systematically investigates how thiol-disulfide interactions influence the structure and mechanical properties of casein gels. Acid gels were prepared from suspensions of micellar casein (MC) powder that were heat-treated at 70 °C. Thiol groups were variably blocked with N-ethylmaleimide (NEM). The gels were characterized using stress-strain measurements, rheological analyses, and confocal microscopy. The stress-strain curves exhibited a biphasic behavior, with an initial linear elastic phase followed by a linear plastic region and a nonlinear failure zone. Compared to control samples, the addition of 100 mM NEM reduced the gel strength by 50%, while G' and G″ increased by around 100%, unexpectedly. NEM-treated gels consist of uniformly sized building blocks coated with a whey protein layer. Strong physical interactions and dense packing enhance viscoelasticity under short deformations but reduce the compressive strength during prolonged loading. In contrast, control samples without NEM demonstrate weak viscoelasticity and increased compressive strength. The former is attributed to a broader particle size distribution from lower acid stability in the untreated gels, while the particularly high compressive strength of heat-treated gels additionally results from disulfide cross-links. The results show that thiol blocking and heating enable the targeted formation of acid casein gels with high shear stability but a low compressive strength.
Keywords: confocal fluorescence microscopy; gels; mechanical characterization; micellar casein powder; milk proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Nguyen B.T., Chassenieux C., Nicolai T., Schmitt C. Effect of the pH and NaCl on the microstructure and rheology of mixtures of whey protein isolate and casein micelles upon heating. Food Hydrocoll. 2017;70:114–122. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.03.013. - DOI
-
- Thill S., Schmidt T., Wöll D., Gebhardt R. A regenerated fiber from rennet-treated casein micelles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2021;299:909–914. doi: 10.1007/s00396-020-04802-5. - DOI
-
- Asaduzzaman M., Gebhardt R. Influence of Post-Treatment Temperature on the Stability and Swelling Behavior of Casein Microparticles. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023;308:2200661. doi: 10.1002/mame.202200661. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

