The Autophagy Inhibitor Bafilomycin Inhibits Antibody-Dependent Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Killing of Breast Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 40650051
- PMCID: PMC12250358
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136273
The Autophagy Inhibitor Bafilomycin Inhibits Antibody-Dependent Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Killing of Breast Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
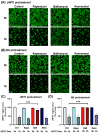
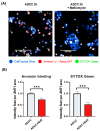
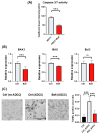
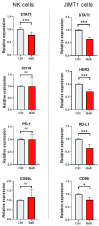
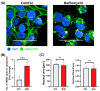
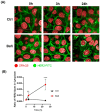
The resistance of breast cancer cells to therapeutic antibodies such as anti-HER2 trastuzumab can be overcome by engaging natural killer (NK) cells for killing antibody-binding tumor cells via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Here, we investigated how autophagy modulation affects trastuzumab-mediated ADCC in HER2-positive JIMT1 breast cancer cells and NK cells. Autophagy inducers (rapamycin and resveratrol) had no significant impact, but the inhibitor bafilomycin nearly abolished ADCC. Protection occurred when either cancer or NK cells were pretreated, indicating dual effects. Bafilomycin reduced phosphatidylserine externalization, the loss of plasma membrane integrity, caspase-3/7 activity, and DNA fragmentation. It downregulated pro-apoptotic BAK1 and BAX without altering BCL-2. Additionally, bafilomycin decreased HER2 surface expression, impairing trastuzumab binding, and modulated immune regulators (STAT1, CD95, and PD-L1) in NK and/or in the cancer cells. Bafilomycin disrupted HER2 trafficking and induced HER2 internalization, leading to its accumulation in cytoplasmic vesicles. These findings show that autophagy inhibition by bafilomycin confers ADCC resistance by altering apoptosis, immune signaling, and HER2 dynamics. The study underscores autophagy's role in antibody-based cancer therapy efficacy.
Keywords: antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; apoptosis; autophagy; natural killer cell; trastuzumab.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

