Investigating Protective Effect of Suspension of Paeoniflorin in Combination with Curcumin Against Acute Liver Injury Based on Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Pathway
- PMID: 40650100
- PMCID: PMC12249775
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136324
Investigating Protective Effect of Suspension of Paeoniflorin in Combination with Curcumin Against Acute Liver Injury Based on Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Pathway
Abstract
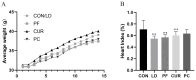
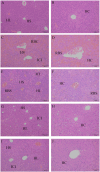
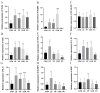
The objective of this study was to formulate a compound suspension comprising paeoniflorin and curcumin, assess its quality characteristics, and investigate its protective efficacy against acute liver injury in mice. The prescriptions were screened using a single-factor test, and nine groups of suspensions were prepared using the dispersion method. Fifty KM mice (four weeks old) were selected and randomly divided into five groups: the CON, LD, PF, CUR, and PC groups. The doses of both paeoniflorin and curcumin were 100 mg/kg BW, and different suspensions were given to different groups by gavage for 14 days. All the groups except the CON group were injected intraperitoneally with 20 μg/kg LPS and 700 mg/kg D-GalN on the last day. According to the results, the suspension prepared using the optimal prescriptions was orange-yellow in color, with homogeneous turbidity and good re-dispersibility. The combination treatment could reduce the severity of pathological injuries of liver, improve the ultrastructure of hepatocytes, increase the activities of T-SOD, GSH-Px, and CAT, decrease the levels of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-1, and down-regulate the expression of genes such as TLR4, MyD88, IκBα, and NLRP3. The underlying mechanism might be associated with the enhancement of antioxidant enzyme activities, inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway, and suppression of inflammasome assembly and release in hepatic tissues.
Keywords: TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3; acute liver injury; curcumin; paeoniflorin; suspension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of Rehmannia glutinosa polysaccharide on LPS-induced acute liver injury in mice and related underlying mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120099. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120099. Epub 2025 Jun 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40484254
-
Ginsenoside Rd protects against acute liver injury by regulating the autophagy NLRP3 inflammasome pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 28;15(1):3569. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87991-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39875579 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of glycolytic metabolic reprogramming and the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway: comparative analysis of anti-inflammatory activity between two dosage forms of Pudilan xiaoyan.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Aug 29;352:120204. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120204. Epub 2025 Jun 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40571230
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Foetal haemoglobin inducers for reducing blood transfusion in non-transfusion-dependent beta-thalassaemias.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 13;1(1):CD013767. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013767.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36637054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ren S., Wang Y., Zhang Y., Yan P., Xiao D., Zhao Y., Jia W., Ding L., Dong H., Wei C., et al. Paeoniflorin alleviates AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy in H9c2 cells by regulating oxidative stress and Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023;165:115253. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115253. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

