PEMFs Restore Mitochondrial and CREB/BDNF Signaling in Oxidatively Stressed PC12 Cells Targeting Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 40650273
- PMCID: PMC12250253
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136495
PEMFs Restore Mitochondrial and CREB/BDNF Signaling in Oxidatively Stressed PC12 Cells Targeting Neurodegeneration
Abstract
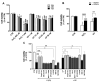
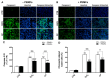
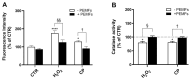
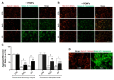
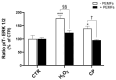
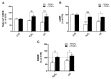
Alzheimer's disease (AD), the most prevalent form of neurodegenerative dementia, is characterized by progressive cognitive decline and neuronal loss. Despite advances in pharmacological treatments, current therapies remain limited in efficacy and often induce adverse effects. Increasing evidence highlights oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and disrupted neurotrophic signaling as key contributors to AD pathogenesis. Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) are emerging as a non-invasive, multifactorial approach with promising biological effects. In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective potential of PEMFs in NGF-differentiated PC12 cells exposed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or amyloid-β peptide (Aβ), both of which model pathological features of AD. PEMF treatment significantly counteracted H2O2- and Aβ-induced cytotoxicity by restoring cell viability, reducing reactive oxygen species production, and improving catalase activity. Furthermore, PEMFs preserved the mitochondrial membrane potential and decreased caspase-3 activation and chromatin condensation. Mechanistically, PEMFs inhibited ERK phosphorylation and enhanced cAMP levels, CREB phosphorylation, and BDNF expression, pathways known to support neuronal survival and plasticity. In conclusion, these findings suggest that PEMFs modulate multiple stress response systems, promoting neuroprotection under oxidative and amyloidogenic conditions.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; BDNF; CREB; ERK; MMP; PC12 cells; PEMFs; cAMP; neuroprotection; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was supported by Igea S.p.A., which provided financial and technical support related to the PEMF device used. However, Igea S.p.A. had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation of the results, or decision to submit the paper for publication. S.S. and R.C. helped in the manuscript’s preparation, specifically in the description of the PEMF stimulation device. S.S. and R.C. were involved in the final proofreading of the manuscript. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
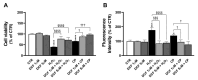
Similar articles
-
Peptides of corn oligopeptides improve Aβ1-42-injured SHSY5Y cells.J Sci Food Agric. 2025 Aug 30;105(11):5738-5750. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.14307. Epub 2025 May 15. J Sci Food Agric. 2025. PMID: 40375668
-
Tartary Buckwheat Peptides Prevent Oxidative Damage in Differentiated SOL8 Cells via a Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis Pathway.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 2;17(13):2204. doi: 10.3390/nu17132204. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40647308 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol Prevents Amyloid Beta-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurotoxicity in Alzheimer's Disease via AMPK-Dependent Suppression of NF-κB Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 27;26(13):6203. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136203. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649980 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the detection and management of motor dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease.Psychiatriki. 2025 Jul 2;36(2):97-100. doi: 10.22365/jpsych.2025.012. Epub 2025 May 14. Psychiatriki. 2025. PMID: 40400272 Review. English, Greek, Modern.
-
Enhancing Neuroprotection Through Exercise: The Synergistic Effects of Bioactive Plant Compounds Via the CREB-BDNF Signaling Pathway.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 30;20(1):69. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10228-z. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40587022 Review.
References
-
- Jurcău M.C., Andronie-Cioara F.L., Jurcău A., Marcu F., Ţiț D.M., Pașcalău N., Nistor-Cseppentö D.C. The Link between Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neuroinflammation in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease: Therapeutic Implications and Future Perspectives. Antioxidants. 2022;11:2167. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112167. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

