Tandem Mass Tags Quantitative Proteomics Reveal the Mechanism by Which Paeoniflorin Regulates the PI3K/AKT and BDNF/CREB Signaling Pathways to Inhibit Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 40650274
- PMCID: PMC12249528
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136498
Tandem Mass Tags Quantitative Proteomics Reveal the Mechanism by Which Paeoniflorin Regulates the PI3K/AKT and BDNF/CREB Signaling Pathways to Inhibit Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
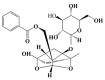
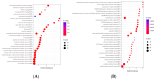
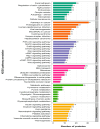
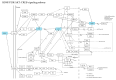
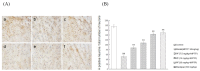
Paeoniflorin (PF), a monomeric compound extracted from the dry roots of Paeonia lactiflora, has been widely used in the treatment of nervous system diseases, marking it as a critical formula in Parkinson's disease (PD). However, the action of PF against PD and its molecular mechanism are still unclear. In this study, tandem mass tags quantitative proteomics was performed to systematically clarify the underlying mechanism of action of PF against PD and to confirm it using in vivo and in vitro studies. The results showed that PF notably enhanced the viability of PC12 cells and mitigated MPP+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Tandem mass tag-based quantitative proteome analysis revealed the identification of 6405 proteins, of which 92 were downregulated and 190 were upregulated. Among them, the levels of PI3K, AKT, CREB, and BDNF in the MPP+-induced PC12 cell and MPTP mice were considerably lower than in the control group, indicating the role of the BDNF/CREB pathway in the pathogenesis of neuroprotection. The related DEP (PI3K, AKT, CREB, and BDNF) expression levels were verified by Western blot. PF effectively restored the altered expression of the four DEPs induced by MPP+ and MPTP. Summarily, PF exerted remarkable neuroprotective effects in MPP+-induced PC12 cell and MPTP-induced mice. Further, our research may provide proteomics insights that contribute to the further exploration of PF as a potential treatment for PD.
Keywords: BDNF/CREB signaling pathway; PI3K/AKT signaling pathway; Parkinson’s disease; paeoniflorin; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







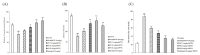

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

