NK Cells: A Powerful Squad Versus SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 40650276
- PMCID: PMC12249530
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136500
NK Cells: A Powerful Squad Versus SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
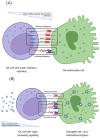
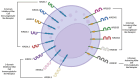
The function of NK cells in cancer and viral infections is well documented and understood. NK cell activity, including cytokine secretion, cytotoxic activity, and the coordination of inhibitory and activating receptors, linking innate and adaptive immunity, among others, has been examined for numerous pathogens, including parasites, bacteria, and viruses. The emergence of the SARS-CoV-2 health crisis has exposed a deficiency in understanding the previously elucidated mechanisms; the rationale for the reported variability in symptomatology among COVID-19 patients is extensive and intricate. It is evident that NK cells exert a significant influence on symptom severity, and their absence, with the presence or absence of their surface receptors, elicits a tailored response to the virus. This overview examines the impact of NK cells on the progression of several viral diseases, emphasizing their involvement in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 via the activation of surface receptors.
Keywords: KIR; NK cells; SARS-CoV-2; lectin-type; receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
A.C.G. has been a speaker of Astra Zeneca; the remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Non-pharmacological measures implemented in the setting of long-term care facilities to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections and their consequences: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 15;9(9):CD015085. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015085.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34523727 Free PMC article.
-
Sero-prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in Ethiopia: Results of the National Population Based Survey, 2021.PLoS One. 2025 May 6;20(5):e0313791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313791. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40327714 Free PMC article.
-
Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 30;1(1):CD006207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006207.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36715243 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity, therapeutic targets and monoclonal antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 infection.PeerJ. 2025 Jun 20;13:e19462. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19462. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40552037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genome-wide shRNA screen uncovers a novel potential ligand for NK cell activating receptors.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1537876. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1537876. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40607388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taborda N.A., Montoya C.J. Las Células Natural Killer y Su Papel En La Respuesta Inmunitaria Durante La Infección Por El Virus de La Inmunodeficiencia Humana Tipo-1. Inmunología. 2014;33:11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.inmuno.2013.11.002. - DOI
-
- Agresti N., Lalezari J.P., Amodeo P.P., Mody K., Mosher S.F., Seethamraju H., Kelly S.A., Pourhassan N.Z., Sudduth C.D., Bovinet C., et al. Disruption of CCR5 Signaling to Treat COVID-19-Associated Cytokine Storm: Case Series of Four Critically Ill Patients Treated with Leronlimab. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021;4:100083. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100083. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

