Activity of Human-Specific Interlaminar Astrocytes in a Chimeric Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome
- PMID: 40650286
- PMCID: PMC12250119
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136510
Activity of Human-Specific Interlaminar Astrocytes in a Chimeric Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome
Abstract
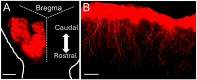
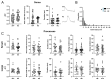
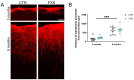
Astrocytes, a subtype of glial cells, have multiple roles in regulating neuronal development and homeostasis. In addition to the typical mammalian astrocytes, in the primate cortex, interlaminar astrocytes are located in the superficial layer and project long processes traversing multiple layers of the cerebral cortex. Previously, we described a human stem cell based chimeric mouse model where interlaminar astrocytes develop. Here, we utilized this model to study the calcium signaling properties of interlaminar astrocytes. To determine how interlaminar astrocytes could contribute to neurodevelopmental disorders, we generated a chimeric mouse model for Fragile X syndrome (FXS). We report that FXS interlaminar astrocytes exhibit hyperexcitable calcium signaling and are associated with dendritic spines with increased turnover rate.
Keywords: astrocytes; calcium; cortex; dendritic spines; iPSC; interlaminar; primate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
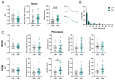

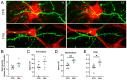
Update of
-
Activity of human-specific Interlaminar Astrocytes in a Chimeric Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 14:2025.02.26.640426. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.26.640426. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 06;26(13):6510. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136510. PMID: 40060700 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

