Defactinib in Combination with Mitotane Can Be an Effective Treatment in Human Adrenocortical Carcinoma
- PMID: 40650315
- PMCID: PMC12249900
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26136539
Defactinib in Combination with Mitotane Can Be an Effective Treatment in Human Adrenocortical Carcinoma
Abstract
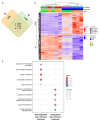
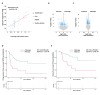
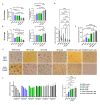
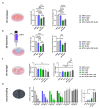
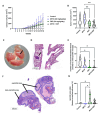
Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is an aggressive cancer with a poor prognosis. Mitotane, the only FDA-approved treatment for ACC, targets adrenocortical cells and reduces cortisol levels. Although it remains the cornerstone of systemic therapy, its overall impact on long-term outcomes is still a matter of ongoing clinical debate. Drug repurposing is a cost-effective way to identify new therapies, and defactinib, currently in clinical trials as part of combination therapies for various solid tumours, may enhance ACC treatment. We aimed to assess its efficacy in combination with mitotane. We tested the combination of mitotane and defactinib in H295R, SW13, and mitotane-sensitive and -resistant HAC15 cells, using functional assays, transcriptomic profiling, 2D and 3D cultures, bioprinted tissues, and xenografts. We assessed drug interactions with NMR and toxicity in vivo, as mitotane and defactinib have never been previously administered together. Genomic data from 228 human ACC and 158 normal adrenal samples were also analysed. Transcriptomic analysis revealed dysregulation of focal adhesion along with mitotane-related pathways. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signalling was enhanced in ACC compared to normal adrenal glands, with PTK2 (encoding FAK) upregulated in 44% of tumour samples due to copy number alterations. High FAK signature scores correlated with worse survival outcomes. FAK inhibition by defactinib, both alone and in combination with mitotane, showed effective anti-tumour activity in vitro. No toxicity or drug-drug interactions were observed in vivo. Combination treatment significantly reduced tumour volume and the number of macrometastases compared to those in the mitotane and control groups, with defactinib-treated tumours showing increased necrosis in xenografts. Defactinib combined with conventionally used mitotane shows promise as a novel combination therapy for ACC and warrants further investigation.
Keywords: 3D model; adrenocortical cancer; defactinib; drug repurposing; focal adhesion signalling; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. The role of all listed funding sources was to provide coverage for the necessary reagents and consumables used during the in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Figures
References
-
- Fassnacht M., Assie G., Baudin E., Eisenhofer G., de la Fouchardiere C., Haak H.R., de Krijger R., Porpiglia F., Terzolo M., Berruti A., et al. Adrenocortical Carcinomas and Malignant Phaeochromocytomas: ESMO-EURACAN Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2020;31:1476–1490. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.08.2099. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sbiera S., Leich E., Liebisch G., Sbiera I., Schirbel A., Wiemer L., Matysik S., Eckhardt C., Gardill F., Gehl A., et al. Mitotane Inhibits Sterol-O-Acyl Transferase 1 Triggering Lipid-Mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Adrenocortical Carcinoma Cells. Endocrinology. 2015;156:3895–3908. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1367. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lerario A.M., Worden F.P., Ramm C.A., Hasseltine E.A., Stadler W.M., Else T., Shah M.H., Agamah E., Rao K., Hammer G.D. The Combination of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor 1 (IGF1R) Antibody Cixutumumab and Mitotane as a First-Line Therapy for Patients with Recurrent/Metastatic Adrenocortical Carcinoma: A Multi-Institutional NCI-Sponsored Trial. Horm. Cancer. 2014;5:232–239. doi: 10.1007/s12672-014-0182-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Landwehr L.-S., Altieri B., Sbiera I., Remde H., Kircher S., Olabe J., Sbiera S., Kroiss M., Fassnacht M. Expression and Prognostic Relevance of PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoints in Adrenocortical Carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024;109:2325–2334. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022-2.1.1-NL-2022-00010/Hungarian Scientific Research Grant of the National Research, Development and Innovation (NRDI) Office Fund of the Ministry of Culture and Innovation under the National Laboratories Program (National Tumour Biology Laboratory
- TKP2021-EGA/TKP2021-NVA/TKP2021-NKTA, MOLORKIV/Hungarian Thematic Excellence Program
- NRDI NKFI-FK135065/National Research, Development and Innovation (NRDI) Office Fund
- ÚNKP-23-5-SE-4/New National Excellence Program of the Ministry of Human Capacities
- BO/00092/21/Bolyai Research Fellowship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

