Circadian rhythms of gut microbiota and plaque vulnerability: mechanisms and chrono-microbiota modulation interventions
- PMID: 40650475
- PMCID: PMC12258220
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2532703
Circadian rhythms of gut microbiota and plaque vulnerability: mechanisms and chrono-microbiota modulation interventions
Abstract
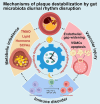
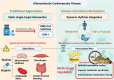
The stability of atherosclerotic plaques constitutes the fundamental pathological basis for acute cardiovascular events, and their circadian rhythm characteristics highlight the essential role of dynamic interactions between the host and microorganisms. This review systematically elucidates the multifaceted mechanisms by which disruptions in the circadian rhythm of the gut microbiota contribute to plaque destabilization. Specifically, the microbiota modulates endothelial function, immune homeostasis, and vascular inflammation via rhythmic variations in metabolites. Perturbations in this rhythm compromise the structural integrity of plaques through a synergistic "metabolic-immune-vascular" network. Furthermore, the review unveils the bidirectional regulation between the host's circadian clock and the microbiota's rhythm. Innovatively, we propose "Chronotherapy-based Microbiome Modulation (CMM)," a strategy that reestablishes synchrony between the host and microbiota rhythms through time-restricted feeding, time-specific probiotics, and drugs targeting the circadian clock, thereby, it is possible to improve plaque stability by regulating the host's gut microbiota. The clinical translation of these findings requires overcoming technical challenges, such as personalized time window prediction and microbiota ecological risk assessment, and integrating multi-omics dynamic monitoring with AI modeling and optimization strategies. This review presents a novel perspective on the regulation of plaque stability.
Keywords: Stability of atherosclerotic plaques; biological clock synchronization; chrono-modulation; circadian rhythm; gut microbiota; host-microbe interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
