Intracellular pathogen effector reprograms host gene expression by inhibiting mRNA decay
- PMID: 40651939
- PMCID: PMC12255788
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61194-2
Intracellular pathogen effector reprograms host gene expression by inhibiting mRNA decay
Abstract
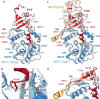
Legionella pneumophila, an intracellular bacterial pathogen, injects effector proteins into host cells to manipulate cellular processes and promote its survival and proliferation. Here, we reveal a unique mechanism by which the Legionella effector PieF perturbs host mRNA decay by targeting the human CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. High-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures and biochemical analyses reveal that PieF binds with nanomolar affinity to the NOT7 and NOT8 catalytic subunits of CCR4-NOT, obstructing RNA access and displacing a catalytic Mg²⁺ ion from the active site. Additionally, PieF prevents NOT7/8 from associating with their partner deadenylases NOT6/6L, inhibiting the assembly of a functional deadenylase complex. Consequently, PieF robustly blocks mRNA poly(A) tail shortening and degradation with striking potency and selectivity for NOT7/8. This inhibition of deadenylation by PieF impedes cell cycle progression in human cells, revealing a novel bacterial strategy to modulate host gene expression.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Eichner, H., Karlsson, J. & Loh, E. The emerging role of bacterial regulatory RNAs in disease. Trends Microbiol.30, 959–972 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Halfmann, A., Kovács, M., Hakenbeck, R. & Brückner, R. Identification of the genes directly controlled by the response regulator CiaR in Streptococcus pneumoniae: five out of 15 promoters drive expression of small non-coding RNAs. Mol. Microbiol.66, 110–126 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Ensminger, A. W. Legionella pneumophila, armed to the hilt: justifying the largest arsenal of effectors in the bacterial world. Curr. Opin. Microbiol.29, 74–80 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Qiu, J. & Luo, Z.-Q. Legionella and Coxiella effectors: strength in diversity and activity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.15, 591–605 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Du Toit, A. The effector repertoire of Legionella. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.17, 126 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

