CX3CL1 promotes M1 macrophage polarization and osteoclast differentiation via NSUN5-mediated m5C modification
- PMID: 40652104
- PMCID: PMC12255738
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-11046-2
CX3CL1 promotes M1 macrophage polarization and osteoclast differentiation via NSUN5-mediated m5C modification
Abstract
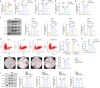
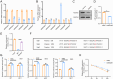
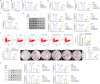
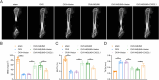
Bone homeostasis refers to a dynamic equilibrium maintained between osteogenesis and osteoclastic bone resorption within the skeletal system. CX3CL1 (Fractalkine) is a chemokine that plays a significant regulatory role in bone homeostasis. This study aimed to investigate the mechanisms by which CX3CL1 regulates bone homeostasis. The expression of CX3CL1 in LPS-stimulated and RANKL-stimulated macrophages was examined using qPCR and Western blotting. Functional studies employed shRNA-mediated knockdown and overexpression of CX3CL1/NSUN5, followed by analysis of pro-inflammatory factor levels(IL-1β, IL-6, iNOS, and TNF-α), M1/M2 markers (CD86/CD206), osteoclast activity (TRAP staining, CTX-1 level), and key osteoclastogenic factors (NFATc1, c-Fos). Potential mechanisms were validated using Methylated RNA Immunoprecipitation (MeRIP), RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP), and Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay experiments. An ovariectomy (OVX)-induced osteoporosis mouse model was used for in vivo validation. Results showed that CX3CL1 was significantly upregulated in LPS- and RANKL-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Knockdown of CX3CL1 inhibited macrophage M1 polarization and osteoclast differentiation. NSUN5 interacted with CX3CL1 and suppressed its stability by promoting the m5C modification of CX3CL1 mRNA. Additionally, Overexpression of CX3CL1 reversed the inhibitory effect of NSUN5 overexpression on macrophage M1 polarization and osteoclast differentiation. In OVX mice, NSUN5 overexpression preserved bone mass (increased BV/TV, reduced Tb.Sp), while CX3CL1 co-expression abolished this protection. In conclusion, CX3CL1 accelerates M1 macrophage polarization and promotes osteoclast differentiation, mechanistically regulated by m5C modification mediated by NSUN5. This study provides novel therapeutic strategies and targets for maintaining bone homeostasis and preventing and treating bone-related diseases.
Keywords: Bone homeostasis; CX3CL1; M1 polarization; NSUN5; Osteoclast differentiation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Songgang People’s Hospital. All animal experiments were complied with the ARRIVE guidelines. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

