Through its genoprotective, mitochondrial bioenergetic modulation, and antioxidant effects, Fucoxanthin and its metabolite minimize Ochratoxin A-induced nephrotoxicity in HK-2 human kidney cells
- PMID: 40652198
- PMCID: PMC12255067
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-025-04276-z
Through its genoprotective, mitochondrial bioenergetic modulation, and antioxidant effects, Fucoxanthin and its metabolite minimize Ochratoxin A-induced nephrotoxicity in HK-2 human kidney cells
Abstract
Background: Ochratoxin A (OTA) is a mycotoxin with reported multiorgan toxicity, especially kidney toxicity. Fucoxanthin (FX) and its hydrolyzed metabolite Fucoxanthinol (FXL) have reno-protective antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. This study evaluates the nephroprotective effects of FX and FLX on OTA-induced renal cytotoxicity using the HK-2 cell line.
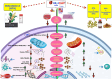
Methods: Molecular docking was used to study the binding affinities with the main proteins of the studied pathways. Various in-vitro assays were used to test the hypothesis, including MTT, mitochondrial bioenergetics, oxidative stress, and apoptosis biomarkers.
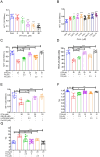
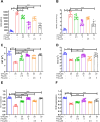
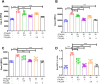
Results: Docking revealed binding affinities of the tested chemicals with mitochondria, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Data showed that OTA has a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect on HK-2 cells. Notably, FX and FXL improved cell viability. A significant deregulation of normal cellular pathways including genotoxicity (DNA damage percentage), mitochondrial bioenergetics disruption (PDH, α-KG, MCI and MCIII complexes activities, ATP levels and mitochondrial membrane potential), downregulation of some mitochondrial genes (ND1, ND5, CO-1 and ATP6/8) expression, mitophagy inhibition (PARK1 and parkin), Oxidative stress induction (ROS and TBARS), oxidative stress genes downregulation (HO-1 and Nrf2), antioxidant enzymatic activity reduction (ROS and CAT), and apoptotic mediator markers elevation (Caspases- 3, 8 and 9, and Bax/Bcl-2 ratio) were observed in OTA mono-treated cells compared to untreated control cells. All parameters were markedly normalized by combining FX or FLX with OTA, providing more protection in FXL co-treated samples.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that FX and FXL may be effective novel therapies for treating OTA-induced nephrotoxicity in vitro.
Keywords: Cellular bioenergetics; Fucoxanthin; Fucoxanthinol; Mitochondria; Nephrotoxicity; Ochratoxin A; Oxidative stress.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics, consent to participate, and consent to publish: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Eskola M, et al. Towards a dietary-exposome assessment of chemicals in food: an update on the chronic health risks for the European consumer. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(11):1890–911. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q, et al. Formation of Furan from Linoleic acid thermal Oxidation:(E, E)-2, 4-Decadienal as a Critical Intermediate Product. J Agric Food Chem. 2024;72(8):4384–92. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

