Pneumonia due to scrub typhus infection: a case report
- PMID: 40652235
- PMCID: PMC12255042
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-025-03827-2
Pneumonia due to scrub typhus infection: a case report
Abstract
Background: Scrub typhus is an acute febrile illness caused by the rickettsial bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi, transmitted to humans through infected mite bites. Patients typically present with sudden onset high fever, headache, myalgia, and eschar formation at the site of the bites. Respiratory symptoms, such as cough and shortness of breath, can also occur, especially in severe cases that lead to pneumonia or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). This report presents a case of scrub typhus pneumonia, diagnosed by metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid(BALF).
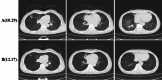
Case presentation: A 58-year-old woman was admitted with cough, sputum production, and fever. Imaging revealed pneumonia. During hospitalization, bronchoscopy was performed to identify the causative pathogen. mNGS of the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid confirmed Orientia tsutsugamushi infection. Patient's pneumonia was improved after oral administration of doxycycline(100 mg two times daily) for 1 month.
Conclusion: This report highlights the diagnostic challenges of scrub typhus-induced pneumonia and demonstrates usefulness and the advantages of mNGS in identifying rare pathogens.
Keywords: Case report; Pneumonia; Scrub typhus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This case report was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Yanbian University, ethics committee approval number:2025142. Consent to participate: Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of images and personal information for this case report. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources