Impact of the initial administration of an antiretroviral drug with latency reversal properties on the HIV reservoir size
- PMID: 40653494
- PMCID: PMC12256594
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-09474-1
Impact of the initial administration of an antiretroviral drug with latency reversal properties on the HIV reservoir size
Abstract
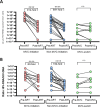
The elimination of the latent viral reservoir remains the main barrier in the quest for a cure for people with HIV (PWH). The administration of latency reversal agents (LRA) at antiretroviral treatment (ART) initiation could improve the effectiveness of strategies aimed at HIV remission. This study assessed the impact of maraviroc (MVC), an antiretroviral drug with HIV latency reversal properties, on the viral reservoir size when it is administered at ART initiation. We conducted a longitudinal observational study in PWH initiating ART with a regimen including (MVC-initiation, n = 12) or not including MVC (non-MVC-initiation, n = 22), or switching to an MVC-containing regimen after achieving an undetectable viral load (VL) (MVC-switch, n = 9). The HIV reservoir size was determined via Alu-LTR and Intact Proviral DNA Assay (IPDA) methods, and cell-associated HIV-RNA (ca-HIV-RNA) by nested-qPCR. Comparative analyses employed mixed multivariate linear models. After a median of 90 weeks, the MVC-initiation group showed a greater reduction in integrated and IPDA-total (7.1- and 4.0-fold, respectively), but not IPDA-intact, HIV-DNA reservoir compared to the non-MVC-initiation group. The reductions in integrated, IPDA-total, and IPDA-intact HIV-DNA levels in the MVC-initiation group were also greater compared to the MVC-switch group (from 5.4 to 13.8-fold). Moreover, no significant differences in the HIV transcriptional activity, assessed by ca-HIV-RNA levels or HIV-RNA/HIV-DNA ratios, were observed between the MVC-initiation and non-MVC-initiation groups. In conclusion, starting ART with a drug with HIV latency reversing activity at detectable VL phase may contribute to a greater reduction in the HIV-DNA reservoir. These findings could inform the design of future trials targeting HIV remission via a "kick and kill" strategy.
Keywords: Antiretroviral Therapy; HIV reservoir; Latency reversal agent; Maraviroc; Timing of administration.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

