Diagnosing pathologic myopia by identifying morphologic patterns using ultra widefield images with deep learning
- PMID: 40653573
- PMCID: PMC12256625
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01849-y
Diagnosing pathologic myopia by identifying morphologic patterns using ultra widefield images with deep learning
Abstract
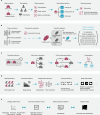
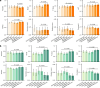
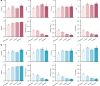
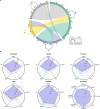
Pathologic myopia is a leading cause of visual impairment and blindness. While deep learning-based approaches aid in recognizing pathologic myopia using color fundus photography, they often rely on implicit patterns that lack clinical interpretability. This study aims to diagnose pathologic myopia by identifying clinically significant morphologic patterns, specifically posterior staphyloma and myopic maculopathy, by leveraging ultra-widefield (UWF) images that provide a broad retinal field of view. We curate a large-scale, multi-source UWF myopia dataset called PSMM and introduce RealMNet, an end-to-end lightweight framework designed to identify these challenging patterns. Benefiting from the fast pretraining distillation backbone, RealMNet comprises only 21 million parameters, which facilitates deployment for medical devices. Extensive experiments conducted across three different protocols demonstrate the robustness and generalizability of RealMNet. RealMNet achieves an F1 Score of 0.7970 (95% CI 0.7612-0.8328), mAP of 0.8497 (95% CI 0.8058-0.8937), and AUROC of 0.9745 (95% CI 0.9690-0.9801), showcasing promise in clinical applications.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
- 32350410397/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- D2301002/Shenzhen Medical Research Funds
- JCYJ20240813112016022/Science, Technology and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality
- JC2022009/Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School Cross-disciplinary Research and Innovation Fund Research Plan
- 207/Bureau of Planning, Land and Resources of Shenzhen Municipality (2022)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

