Inhibition of FOXM1 Synergizes with BH3 Mimetics Venetoclax and Sonrotoclax in Killing Multiple Myeloma Cells through Repressing MYC Pathway
- PMID: 40654055
- PMCID: PMC12499415
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202508822
Inhibition of FOXM1 Synergizes with BH3 Mimetics Venetoclax and Sonrotoclax in Killing Multiple Myeloma Cells through Repressing MYC Pathway
Abstract
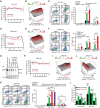
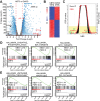
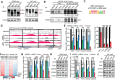
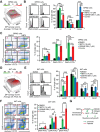
Relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) remains the leading cause of MM mortality. FOXM1 is strongly associated with RRMM, making it a compelling therapeutic target. Through three low-throughput screenings, we have identified nine FDA-approved drugs, including the BH3 mimetic Venetoclax, that synergize with FOXM1 inhibitor NB73 in killing MM cells. Venetoclax has shown effects in 6% of non-t(11;14) and 27% of t(11;14) MM cases. The NB73-Venetoclax combination barely induces acute toxicity in vivo and represses MM cells in vivo and ex vivo. NB73 enhances the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of FOXM1, an effect further amplified by Venetoclax. The NB73-Venetoclax combination abolishes FOXM1's binding to promoters of key MYC pathway genes, such as PLK1, leading to significant downregulation of their expression. Furthermore, the PLK1-specific inhibitor GSK461364 synergizes with NB73 to inhibit MM cell growth. Interestingly, NB73 does not sensitize U266 cells, a Venetoclax-resistant t(11;14) MM cell line expressing high FOXM1, to Venetoclax treatment, which is corrected by a new-generation BH3 mimetic Sonrotoclax and ALK inhibitor Ceritinib. Collectively, targeting FOXM1 demonstrates significant potential for enhancing the efficacy of FDA-approved drugs in RRMM. These findings shed new light on the discouraging outcomes of the Phase-III CANOVA study centering Venetoclax with an encouraging molecular clue.
Keywords: drug resistance; foxm1 inhibitors; multiple myeloma; myc pathway; venetoclax and sonrotoclax.
© 2025 Marshfield Clinic Research Institute and The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
B.S.K., J.A.K. and S.H.K. are co‐inventors on patents filed by the University of Illinois to cover the FOXM1 inhibitor compounds described in this paper. B.S.K. and J.A.K, are members of the Scientific Advisory Board of Celcuity. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- ACS , Cancer Facts and Figures, American Cancer Society, Atlanta, Georgia, 2025.
-
- ACS , Cancer Facts and Figures, American Cancer Society, Atlanta, Georgia, 2020.
-
- Van Oekelen O., Nath K., Mouhieddine T. H., Farzana T., Aleman A., Melnekoff D. T., Ghodke‐Puranik Y., Shah G. L., Lesokhin A., Giralt S., Thibaud S., Rossi A., Rodriguez C., Sanchez L., Richter J., Richard S., Cho H. J., Chari A., Usmani S. Z., Jagannath S., Shah U. A., Mailankody S., Parekh S., Blood 2023, 141, 756. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA268183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA014520/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- CA189956/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 284000/Marshfield Clinic Research Foundation
- GM-130715/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 284010/Marshfield Clinic Research Foundation
- CA268183/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA151354/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- BCRF-083/Breast Cancer Research Foundation
- UG1 CA189956/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA151354/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- OD-037636/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
