A novel protocol for parametrization of a beam model for small stereotactic beams
- PMID: 40654326
- PMCID: PMC12257346
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.70158
A novel protocol for parametrization of a beam model for small stereotactic beams
Abstract
Introduction: Most Treatment Planning Systems (TPS) utilize parameterized multi-source models to represent the radiation beam of linacs. However, small stereotactic beams require special attention due to the importance of correct spot- and field-size definition. The purpose of this work is to develop a protocol for configuring a beam model that provides accurate representation of stereotactic beams.
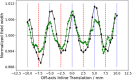
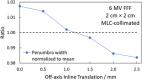
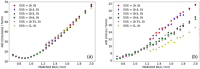
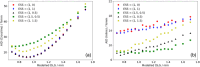
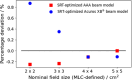
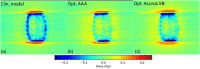
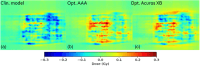
Material and methods: 6 MV flattening filter free (FFF) dose-profiles were measured for Millennium multileaf collimator (MLC)-collimated field sizes (2 × 2 cm2-5 × 5 cm2). They served as a reference against which corresponding TPS-profiles were optimized by configuring the Dosimetric Leaf Gap (DLG) and the Effective Spot Size (ESS). The optimized model was evaluated by comparing calculated and measured stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT)-plans. The proposed protocol was implemented on Anisotropic Analytical Algorithm (AAA) and Acuros XB in the Eclipse TPS.
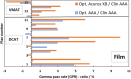
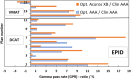
Results: Improvement in the agreement between measured and modelled profiles are identified using the suggested protocol. The DLG was determined at an optimum of 0.9 mm for both models whereas the ESS was determined to be (0.5, 0) mm and (1, 0,5) mm for AAA and Acuros XB, respectively. Compared to the standardly configured clinical model, the optimized AAA (Acuros XB) model showed an average improvement in gamma pass-rates of 2% (3%) with film measurements.
Conclusions: The standard protocol for TPS commissioning was shown to produce a sub-optimal beam model for small treatment volumes. The proposed protocol in this work results in a better modelling of small stereotactic beams.
Keywords: beam‐model optimization; dosimetric leaf gap; effective spot size; linac stereotactic radiotherapy.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of The American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following, which may be considered as potential competing interests: During the final phase of reviewing the initial manuscript, Tim Melhus was employed by RaySearch Laboratories.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the accuracy of an enhanced MLC leaf model for Linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Jul;26(7):e70143. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70143. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40653786 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric Comparison between Acuros XB (AXB) and Anisotropic Analytical Algorithm (AAA) in Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 May 1;24(5):1677-1685. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.5.1677. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37247288 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of two-dimensional dosimetric leaf gap on SRS-VMAT for single-isocenter multi-target brain metastases.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 13;15(1):29627. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14300-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40804092 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for early-stage lung cancer: a systematic review on the choice of photon energy and linac flattened/unflattened beams.Radiat Oncol. 2024 Jan 2;19(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13014-023-02392-4. Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38167095 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of flattening-filter-free beam in stereotactic body radiation therapy planning and treatment: A systematic review with meta-analysis.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2017 Jun;61(3):379-387. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.12583. Epub 2017 Jan 24. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28116813
References
-
- De martino F, Clemente S, Graeff C, Palma G, Cella L. Dose calculation algorithms for external radiation therapy: an overview for practitioners. App Sci. 2021;11(15). doi: 10.3390/app11156806 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

