This is a preprint.
Small molecule inhibition of CPSF3 impacts R-loop distribution and abundance
- PMID: 40654756
- PMCID: PMC12248124
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.07.652284
Small molecule inhibition of CPSF3 impacts R-loop distribution and abundance
Abstract
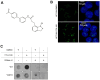
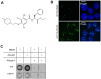
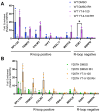
R-loops are three-stranded nucleic acid structures consisting of an RNA/DNA hybrid and a displaced strand of DNA. These structures have been implicated in a variety of regulatory cellular processes. Their untimed or excess accumulation, however, can cause genomic instability and induce DNA damage. Most R-loops form co-transcriptionally when the nascent transcript reanneals to unwound DNA duplex. Changes in the rate of transcription have the potential to impact R-loop formation, and compounds that modulate R-loop formation would be useful molecular tools and therapeutic leads. Cleavage and Polyadenylation Specific Factor 3 (CPSF3) recognizes the pre-mRNA 3' cleavage site, cleaves the transcript prior to polyadenylation, and has been linked to R-loop formation. Inhibition of CPSF3 has been found to induce transcriptional readthrough and cell proliferation defects. A previous report suggested that inhibition of CPSF3 with a small molecule causes a global increase in R-loop abundance. Here we test the impact of YT-II-100, a novel inhibitor of CPSF3. We find that addition of YT-II-100 increases global R-loop formation but does not change R-loop formation at specific genes that are normally used as positive controls for R-loop formation. We performed parallel assays using previously reported compound JTE-607 and observed similar results. Our data emphasize the need for cautious interpretation of experiments using JTE-607 and YT-II-100. There may be different mechanisms of R-loop formation depending on gene loci, with the control of R-loop formation at some genes diverging from the regulation of global R-loop formation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
