Hidradenitis suppurativa and daily lifestyle
- PMID: 40655135
- PMCID: PMC12245869
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1627638
Hidradenitis suppurativa and daily lifestyle
Abstract
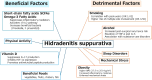
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that significantly impairs quality of life. While its pathogenesis involves genetic, immunologic, and environmental components, emerging evidence highlights the substantial impact of modifiable lifestyle factors on disease onset and progression. This review summarizes the current understanding of how lifestyle-related elements interact with the inflammatory milieu in HS. Beneficial factors, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamin D, play a protective role by suppressing proinflammatory cytokines, enhancing antimicrobial responses, and promoting the growth of beneficial gut microbiota. Diets rich in vegetables, fruits, chicken, and fish are supportive in maintaining immune balance. Conversely, detrimental factors, including smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, and sleep disorders, are associated with heightened inflammatory responses, increased disease severity, and higher recurrence rates. Understanding these lifestyle-related influences provides a foundation for non-pharmacologic, adjunctive interventions aimed at mitigating disease burden. Comprehensive management of HS should therefore include lifestyle modification as a key component to improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: diet; hidradenitis suppurativa; lifestyle factors; physical activity; smoking.
Copyright © 2025 Saito-Sasaki and Sawada.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of the real-world application of the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Quality of Life (HiSQOL) score to adults with hidradenitis suppurativa.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jan 24;192(2):261-268. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae367. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39374841
-
The roles of interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-17F in hidradenitis suppurativa pathogenesis: evidence from human in vitro preclinical experiments and clinical samples.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Mar 18;192(4):660-671. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae442. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39531733 Clinical Trial.
-
Bimekizumab for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa.Immunotherapy. 2024;16(16-17):1005-1013. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2024.2401308. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Immunotherapy. 2024. PMID: 39297706 Review.
-
Relationship of vitamin D to pathogenesis and outcomes of hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Nov 16;317(1):29. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03534-8. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39549121
-
The Burden of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Signs and Symptoms in Quality of Life: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jun 22;18(13):6709. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18136709. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34206415 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical