Lactate and lactylation: emerging roles in autoimmune diseases and metabolic reprogramming
- PMID: 40655145
- PMCID: PMC12245685
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1589853
Lactate and lactylation: emerging roles in autoimmune diseases and metabolic reprogramming
Abstract
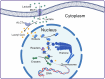
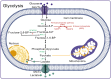
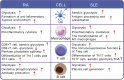
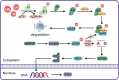
Autoimmune diseases are a set of conditions in which the immune system incorrectly identifies and attacks the body's own healthy tissue, severely compromising patient health. While current treatments can somewhat control disease progression, their long-term effectiveness remains limited, necessitating the development of more effective therapeutic approaches. Lactate and lactylation are critical links between metabolic reprogramming and epigenetics. As an emerging epigenetic modification, lactylation induced by lactate is closely associated with the onset of autoimmune diseases. Lactylation can be categorized into histone and nonhistone modifications, both of which play pivotal roles in cellular functions and pathophysiological processes through distinct regulatory mechanisms. Lactylation impacts immune cell function by regulating metabolic reprogramming and signaling pathways. In autoimmune diseases, immune cell metabolic reprogramming controls lactylation levels through metabolic byproducts, and lactylation, in turn, modulates the cellular metabolism by altering the transcription and structure of key enzymes. These interconnected processes collectively drive disease progression. To better understand the role of lactate and lactylation in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, this review synthesizes the effects on specific immune cells, examining their dual effects on immune system function and their particular impacts on two common autoimmune diseases-rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). By combining the established role of lactate in immune metabolic reprogramming with the emerging understanding of the influence of lactate-induced lactylation on epigenetic regulation, this paper explores the relationship between lactylation and the progression of autoimmune diseases. This approach aims to enhance the understanding of the interplay between epigenetics and metabolism in autoimmune disease development, providing new perspectives for future therapeutic strategies. Studies collectively indicate that treatment can be improved through regulating key enzymes involved in lactylation, targeting lactate production pathways, integrating innovative approaches with current therapies, and adopting personalized treatment strategies.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; epigenetics; lactate; lactylation; metabolic reprogramming.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Yang, Zhan, Yang, Zeng, Chen, Zeng, Hu, Hu, Xiao, Shao and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Research progress on the interaction between glucose metabolic reprogramming and lactylation in tumors.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 14;16:1595162. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1595162. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40755753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactate and lactylation modifications in neurological disorders.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Jun 19. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01344. Online ahead of print. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 40537007
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Aerobic exercise-induced lactate production: a novel opportunity for remodeling the tumor microenvironment.Front Genet. 2025 Jul 9;16:1620723. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1620723. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40704062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

