Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Different Irrigants Mixed with Silver Nanoparticles - An In Vivo Study
- PMID: 40655752
- PMCID: PMC12244568
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_186_25
Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Different Irrigants Mixed with Silver Nanoparticles - An In Vivo Study
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the antimicrobial efficacy of different irrigants combined with silver nanoparticles.
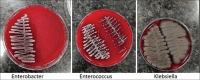
Materials and methods: Thirty-five patients were divided into seven groups (two control and five experimental), including Group 1: negative control (normal saline), Group 2: positive control (sodium hypochlorite), and Group 3 (sodium hypochlorite + AgNP), Group 4 (Twin Kleen), Group 5 (Twin Kleen + AgNP), Group 6 (Q Mix), and Group 7 (Q Mix + AgNP). Pre- and post-treatment bacterial samples were collected for analysis.
Results: Sodium hypochlorite combined with silver nanoparticles demonstrated the highest antimicrobial efficacy among the tested irrigants, with a significant difference confirmed by the Chi-square statistical analysis.
Conclusion: Within the limitations of the study, it can be concluded that sodium hypochlorite when mixed with the silver nanoparticles showed higher antimicrobial efficacy as compared to the other tested groups.
Keywords: Antimicrobial efficacy; Q Mix; Twin Kleen; root canal irrigants; silver nanoparticles; sodium hypochlorite.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Irrigants for non-surgical root canal treatment in mature permanent teeth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD008948. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008948.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972129 Free PMC article.
-
Tooth discoloration caused by nanographene oxide as an irrigant and intracanal medicament in the endodontic treatment of extracted single-rooted teeth: An ex-vivo study.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 26;20(6):e0325430. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325430. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40569948 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial action, cytotoxicity and erosive potential of hypochlorous acid obtained from an electrolytic device compared with sodium hypochlorite.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Apr 29;28(5):282. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05675-6. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38683234
-
Pulp tissue dissolution capacities of two hypochlorite-based irrigants at different temperatures: an in vitro study.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Jul 5;25(1):1104. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06516-y. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40618078 Free PMC article.
-
Antiseptics for burns.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 12;7(7):CD011821. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011821.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28700086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma R, Panadan J, Sharma M, Tanweer S. Antimicrobial effectiveness of different root canal irrigants on viability of root canal flora. J Clin Diagn Res. 2023;17:37–41. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2023/59877.17505.
-
- Wu D, Fan W, Kishen A, Gutmann JL, Fan B. Evaluation of the antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis biofilm. J Endod. 2014;40:285–90. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.08.022. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources