Research progress of ECT2 and RhoA-related signaling pathways in gynecological tumors
- PMID: 40655948
- PMCID: PMC12246546
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1602649
Research progress of ECT2 and RhoA-related signaling pathways in gynecological tumors
Abstract
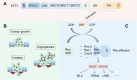
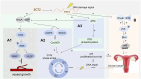
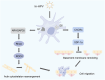
Epithelial Cell Transformation Factor 2 (ECT2) is highly expressed in a variety of cancers, including gynecological tumors. The mislocalization of ECT2 can abnormally activate Ras homolog family member A (RhoA) in the Ras homolog gene family (Rho) Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factor (GEF) family. Activated RhoA binds to Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK), phosphorylates various target proteins, triggers a cascade reaction, regulates the functions of downstream proteins, and thereby plays an important role in the occurrence and development of tumors. This article reviews the roles of ECT2 and RhoA/ROCK signaling pathways in ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, and endometrial cancer, and summarizes and discusses the research progress of downstream molecules, transduction pathways, and mechanisms related to them. Through comprehensive analysis and summary of the current research results, it is revealed that the ECT2/RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway and related crosstalk pathways play an important role in the occurrence, development, and metastasis of gynecological tumors. This article aims to provide a basis for related research and offer relevant references for the treatment of gynecological tumors in the future.
Keywords: Ect2; ROCK; RhoA; cervical cancer; endometrial cancer; ovarian cancer.
Copyright © 2025 Sheng, Liang, Wang, Zhou, Xie, Ke and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

