Macrophages as Multifaceted Orchestrators of Tissue Repair: Bridging Inflammation, Regeneration, and Therapeutic Innovation
- PMID: 40655959
- PMCID: PMC12255350
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S527764
Macrophages as Multifaceted Orchestrators of Tissue Repair: Bridging Inflammation, Regeneration, and Therapeutic Innovation
Abstract
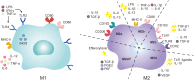
Macrophages play pivotal roles in tissue repair through remarkable functional plasticity, orchestrated by their developmental origins and local microenvironmental cues. Embryonically derived resident macrophages primarily maintain tissue homeostasis, while monocyte-derived macrophages respond predominantly to inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling. Effective tissue repair requires precise temporal regulation of macrophage polarization, balancing inflammation resolution, angiogenesis, and scar formation. Metabolic reprogramming further enhances macrophage plasticity, enabling adaptation to fluctuating energy demands at injury sites. Emerging evidence also highlights that macrophages integrate biomechanical forces-such as matrix stiffness and shear stress-with biochemical signals to fine-tune their inflammatory and reparative programs. Recognizing this mechanoregulation broadens therapeutic avenues for precisely modulating macrophage behavior in regenerative medicine. Targeting macrophage subsets, polarization states, or metabolic pathways has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy to optimize healing outcomes. However, the inherent complexity of macrophage heterogeneity presents considerable challenges to therapeutic precision. This review systematically summarizes the multifaceted roles of macrophages in tissue repair, emphasizing how developmental origins dictate functional specificity, dynamic phenotypic transitions, and metabolic adaptability, aiming to advance macrophage-based precision therapeutics for regenerative medicine.
Keywords: macrophage; macrophage polarization; therapeutic strategy; tissue repair.
© 2025 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immunometabolism of macrophages in the bone microenvironment: a new perspective for bone healing therapy.J Adv Res. 2025 Jul 29:S2090-1232(25)00576-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2025.07.046. Online ahead of print. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 40744273 Review.
-
Leptin Enhances M1 Macrophage Polarization and Impairs Tendon-Bone Healing in Rotator Cuff Repair: A Rat Model.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 May 1;483(5):939-951. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003428. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39982019
-
Macrophage Signaling Pathways in Health and Disease: From Bench to Bedside Applications.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jun 16;6(7):e70256. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70256. eCollection 2025 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40529613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechano-immunomodulation of macrophages influences the regenerative environment of fracture healing through the regulation of angiogenesis and osteogenesis.Acta Biomater. 2025 Jun 15;200:187-201. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.05.045. Epub 2025 May 21. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40409508
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

