Transmission and therapeutic modalities on condyloma acuminata in children: a case report
- PMID: 40656145
- PMCID: PMC12245637
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2025.50.101.45681
Transmission and therapeutic modalities on condyloma acuminata in children: a case report
Abstract
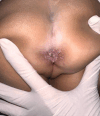
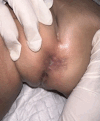
This case report presents a unique instance of condyloma acuminata in a one-year-old child, which adds to the scientific literature by highlighting the potential for non-sexual transmission in pediatric patients. The child exhibited a rapidly enlarging, skin-colored lump around the anus, initially a small bump that soon resembled a cauliflower. Acetowhite testing was positive, and histopathological examination revealed hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis, leading to the diagnosis of condyloma acuminata. The main therapeutic intervention involved the application of 90% trichloroacetic acid (TCA), resulting in complete lesion resolution after two treatments, with no recurrence observed over a six-month follow-up period. This case emphasizes the urgent need for special attention to sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in children, considering the potential link to sexual violence. It highlights the critical, holistic role of venereology specialists, not only in providing effective and safe curative treatments but also in actively preventing further transmission and supporting vulnerable patients like children.
Keywords: Condyloma acuminata; case report; children; sexual violence; trichloroacetic acid.
Copyright: Nissa Avina Pilar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sindhuja T, Bhari N, Gupta S. Asian guidelines for condyloma acuminatum. J Infect Chemother. 2022 Jul;28(7):845–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical