Distal intracranial artery pseudoaneurysm causing subdural hematoma: An illustrative case and a systematic review
- PMID: 40656504
- PMCID: PMC12255207
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_186_2025
Distal intracranial artery pseudoaneurysm causing subdural hematoma: An illustrative case and a systematic review
Abstract
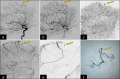
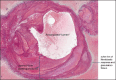
Background: Pseudoaneurysm arising from the distal segment of an intracranial artery is a rare cause of subdural hematoma (SDH). We report a patient diagnosed with a pseudoaneurysm of a cortical branch of the distal anterior cerebral artery (ACA) during planned middle meningeal artery embolization for SDH and present a systematic review to summarize the present literature.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted across EMBASE, MEDLINE, CINAHL, the Cochrane Library, and Scopus to identify studies reporting SDH due to pseudoaneurysms in the terminal intracranial artery segments. Details regarding clinical presentation, management, and outcomes were extracted.
Results: Twenty patients from the 18 retrospective studies and the patient from the present report were included in the review. The mean age of the patients was 49.4 years; 80.9% of the patients were males. A history of nonpenetrating head trauma was present in 11 (52.4%) patients. The most common presenting symptoms were hemiparesis and altered mental status. Catheter angiography established the diagnosis in the majority of the patients (85.7%). Angiography was performed due to a clinical/radiological suspicion for a pseudoaneurysm in 6 (28.5%) patients. In the majority of the patients (66.7%), angiography was performed for a different indication. Middle cerebral artery (15 patients, 71.4%) was the most common location of the pseudoaneurysm, followed by ACA, posterior cerebral artery, and posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Pseudoaneurysm was treated surgically in 14 patients (66.7%) and by endovascular modalities in 5 patients (23.8%). One patient undergoing endovascular treatment required surgical evacuation of SDH. The majority of the patients in both treatment groups (surgical - 72.7%, endovascular - 80%) recovered without severe disability (modified Rankin Scale ≤ 4).
Conclusion: Pseudoaneurysms of distal segments of intracranial arteries are a very rare cause of SDH. A high index of suspicion is required for their identification. While a definitive diagnosis requires catheter angiography, indications to perform angiography in SDH are unclear. Pseudoaneurysms with SDH can be treated safely with both microsurgical and endovascular modalities. Microsurgery has the advantage of draining SDH at the same time. The relative efficacy of different treatment approaches and the indications for each are not yet defined.
Keywords: Endovascular; Microsurgery; Pseudoaneurysm; Subdural hematoma; Trauma.
Copyright: © 2025 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Surgery for epilepsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 1;(7):CD010541. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010541.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jun 25;6:CD010541. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010541.pub3. PMID: 26130264 Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Acosta C, Williams PE, Jr, Clark K. Traumatic aneurysms of the cerebral vessels. J Neurosurg. 1972;36:531–6. - PubMed
-
- Bassett RC, Lemmen LJ. Subdural hematoma associated with bleeding intracranial aneurysm. J Neurosurg. 1952;9:443–50. - PubMed
-
- Bergstrom K, Hemmingsson A. False cortical aneurysm in subdural hematoma following head injury without fracture. Acta Radiol Diagn. 1973;14:657–61. - PubMed
-
- Cho WS, Batchuluun B, Lee SJ, Kang HS, Kim JE. Recurrent subdural hematoma from a pseudoaneurysm at the cortical branch of the middle cerebral artery after mild head injury: Case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2011;51:217–21. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
