Effectiveness of recombinant zoster vaccine in reducing herpes zoster incidence and all-cause mortality among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a retrospective cohort study of 21,046 individuals from TriNetX U.S. Collaborative Network
- PMID: 40656648
- PMCID: PMC12246860
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103319
Effectiveness of recombinant zoster vaccine in reducing herpes zoster incidence and all-cause mortality among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a retrospective cohort study of 21,046 individuals from TriNetX U.S. Collaborative Network
Abstract
Background: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at increased risk of developing herpes zoster (HZ). This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) in reducing both the incidence of HZ and all-cause mortality among individuals with RA.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the TriNetX U.S. Collaborative Network between October 1, 2017 and March 31, 2024. The study population consisted of patients with RA who received RZV (RA-RZV cohort) and those who did not (RA control cohort). Propensity score matching (PSM) was employed to balance baseline characteristics between the groups, accounting for demographics, social economic status, lifestyles, medical utilization, comorbidities, and medications. The primary outcomes were the risk of HZ and all-cause mortality. PSM-adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated using Cox proportional hazards regression models. Kaplan-Meier curves and Log-Rank tests were used to evaluate survival differences.
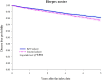
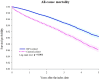
Findings: After PSM, each cohort included 21,046 individuals. The RA-RZV group demonstrated significantly lower risks of HZ (HR: 0.836, 95% CI: 0.738-0.947) and all-cause mortality (HR: 0.606, 95% CI: 0.561-0.654). The HZ risk reduction was more pronounced in patients aged 50-64 years (HR: 0.731, 95% CI: 0.610-0.876), females (HR: 0.791, 95% CI: 0.684-0.915), White (HR: 0.808, 95% CI: 0.696-0.937), and Black/African American participants (HR: 0.685; 95% CI: 0.481-0.976).
Interpretation: RZV vaccination is associated with a reduced risk of HZ among patients with RA aged 50 years and older. While we observed a reduction in all-cause mortality among RZV recipients, this finding should be interpreted with caution, as the effect size may not be entirely attributable to HZ prevention alone. Given the established efficacy of RZV in preventing HZ and its potential to reduce mortality, vaccination should be prioritized among eligible patients with RA.
Funding: There is no funding.
Keywords: Herpes zoster; Mortality; Recombinant zoster vaccine; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Di Matteo A., Bathon J.M., Emery P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2023;402(10416):2019–2033. - PubMed
-
- Safiri S., Kolahi A.A., Hoy D., et al. Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(11):1463–1471. - PubMed
-
- de Almeida A.L.B., Guimarães M., da Costa Pinto M.R., et al. Predictors of serious infections in rheumatoid arthritis-a prospective Brazilian cohort. Adv Rheumatol. 2024;64(1):23. - PubMed
-
- Asada H. Recent topics in the management of herpes zoster. J Dermatol. 2023;50(3):305–310. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous