Electrospun PVA/Co3O4 Nanofibers: A Sustainable Catalyst for Peroxymonosulfate-Mediated Degradation of Tetracycline
- PMID: 40657116
- PMCID: PMC12242669
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01013
Electrospun PVA/Co3O4 Nanofibers: A Sustainable Catalyst for Peroxymonosulfate-Mediated Degradation of Tetracycline
Abstract
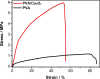
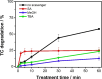
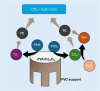
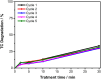
This study develops a poly-(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) nanofiber incorporated with cobalt oxide (Co3O4) for catalytic degradation of antibiotics using peroxymonosulfate (PMS) to generate sulfate radical (SO4 •-) (E° = 2.5-3.1 V vs NHE). These radicals efficiently degrade tetracycline through selective oxidation, offering advantages over conventional hydroxyl radical-based processes. The nanofiber fabrication involved electrospinning of PVA (8% w/v) containing cobalt oxide suspension (5 g L-1) and citric acid (15% w/w polymer). Thermal cross-linking at 160 °C for 2 h enhanced the material's aqueous stability and mechanical properties. Scanning electron microscopy revealed uniform fibers (627-645 nm diameter), while X-ray diffraction, thermal analyses, and spectroscopy confirmed increased crystallinity in PVA/Co3O4 composites. Optimization studies through factorial design identified pH and PMS concentration as key parameters, achieving 60% tetracycline degradation within 60 min. The successful integration of Co3O4 into biodegradable PVA nanofibers presents a sustainable, cost-effective approach for water treatment applications, particularly targeting emerging pharmaceutical contaminants.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures








References
-
- Li S., Wu Y., Zheng H., Li H., Zheng Y., Nan J., Ma J., Nagarajan D., Chang J. S.. Antibiotics Degradation by Advanced Oxidation Process (AOPs): Recent Advances in Ecotoxicity and Antibiotic-Resistance Genes Induction of Degradation Products. Chemosphere. 2023;311:136977. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136977. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
