Botulinum Toxin A Therapy for Glabellar Lines Improves Emotional States: Evaluation of 47 Cases without Mental Disorders
- PMID: 40657169
- PMCID: PMC12240690
- DOI: 10.53045/jprs.2023-0057
Botulinum Toxin A Therapy for Glabellar Lines Improves Emotional States: Evaluation of 47 Cases without Mental Disorders
Abstract
Objectives: Facial wrinkle treatment using botulinum toxin A (BT-A) is an extremely popular aesthetic procedure. Many studies have been conducted on the improvement of the mental states of depressive patients whose glabellar lines were treated with BT-A. It could be caused by afferent effects derived from the proprioception of related facial muscles, which is known as facial feedback hypothesis. This study highlights the impact of BT-A injections into the glabellar region on the emotional states of participants who have specifically no mental disorders.
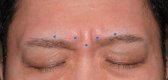
Methods: A total of 47 Asian participants (42 women and 5 men) without mental disorders completed the Japanese version of the Brief, Momentary Mood Checklist (BMC-J) before and 2 weeks after receiving the treatment for glabellar lines with BT- A injections.
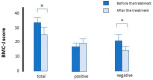
Results: Based on BMC-J scores reported by the participants, their emotional states statistically improved after treatment (P = 0.008), particularly in the concurrent decrease in negative emotions (P = 0.003).
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the first study of the statistically significant effect of the BT-A treatment on the emotional state of subjects without mental disorders. The experiences of emotions derived from the motions of the frown muscles, which may be caused by the modulation of the amygdala activity, are not so complicated but extremely primitive, such as pleasure and unpleasure. This might be the reason why our results of BMC-J, which is used to measure basic emotions, indicated more clearly that negative emotions reduced compared with positive ones, in contrast to the finding of previous published reports that measured more complicated emotions such as feelings.
Keywords: amygdala; botulinum toxin A; emotional state; facial feedback hypothesis; frown muscles.
© 2025 The Japan Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cosmetic Surgery National Data Bank Statistics Date Base 2022. 2023 Dec- [cited 2024 Jan 8]. [Internet]. Available from: https://cdn.theaestheticsociety.org/media/statistics/2022TheAestheticSoc...
-
- 2022 ASPS Procedural Statistics Release Date Base. 2023 Sep- [cited 2024 Jan 8]. [Internet]. Available from: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2022/plastic-su...
-
- Hambleton P. Clostridium botulinum toxins: a general review of involvement in disease, structure, mode of action and preparation for clinical use. J Neurol. 1992 Jan;239(1):16-20. - PubMed
-
- Carruthers J, Carruthers A. A Prospective, randomized, parallel group study analyzing the effect of BTX-A (Botox) and nonanimal sourced hyaluronic acid (NASHA, Restylane) in combination compared with NASHA (Restylane) alone in severe glabellar rhytides in adult female subjects: treatment of severe glabellar rhytides with a hyaluronic acid derivative compared with the derivative and BTX-A. Dermatol Surg. 2003 Aug;29(8):802-9. - PubMed

