Advances of HDAC inhibitors in tumor therapy: potential applications through immune modulation
- PMID: 40657246
- PMCID: PMC12245688
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1576781
Advances of HDAC inhibitors in tumor therapy: potential applications through immune modulation
Abstract
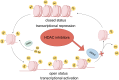
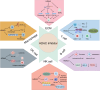
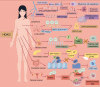
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDAC inhibitors, HDACi) have garnered considerable attention due to their potential in treating various types of malignant tumors. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) not only influence chromatin structure and gene transcription by regulating histone acetylation status but also acetylate various non-histone proteins. They are widely involved in several key biological processes, such as cell cycle regulation, apoptosis induction, and immune responses. HDACi exert their effects by inhibiting HDAC activity; however, these effects are highly concentration-dependent and non-selective. HDACi inevitably disrupt both gene expression and signaling networks, leading to multi-target, non-specific biological effects. This article focuses on the immunomodulatory mechanisms of HDACi, including their role in remodeling the tumor extracellular matrix and their impact on various immune cell populations. The synergistic potential of combining HDACi with other therapeutic approaches is also discussed. This review examines the application of HDACi across different tumor types, highlighting preclinical and clinical evidence that demonstrates the multifunctionality and efficacy of HDACi. By leveraging their unique mechanism of action, HDACi opens new avenues for enhancing antitumor immunity and achieving durable therapeutic responses. Future research and clinical trials will play a crucial role in optimizing the use of HDACi, elucidating resistance mechanisms, and identifying the most effective combinations to maximize patient benefit.
Keywords: HDACi; combination therapy; immunotherapy; tumor microenvironment; tumor therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Tian, Han, Song, Liu, Shen and Zhong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Contribution of histone deacetylases (HDACs) to the regulation of histone and non-histone proteins: implications for fibrotic diseases.BMB Rep. 2025 Jul 10:6322. Online ahead of print. BMB Rep. 2025. PMID: 40635201
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

