Empagliflozin Use in Cardiac Transplant Patients: Real-world experience from Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 40657462
- PMCID: PMC12255340
- DOI: 10.18295/squmj.10.2024.057
Empagliflozin Use in Cardiac Transplant Patients: Real-world experience from Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Objectives: Sodium-glucose transport protein 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are used in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes. Besides their beneficial metabolic effects, such as lowering glycated haemoglobin, body weight and blood pressure, these agents have shown favourable and protective effects on both the heart and kidneys. Notably, these cardio-renal benefits are even seen in individuals without diabetes. However, there is limited evidence regarding the safety and efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors in cardiac transplant recipients. This study aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of empagliflozin in cardiac transplant recipients with diabetes.
Methods: This retrospective study was conducted at the King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, from June 2003 to May 2024. Patients from the cardiac transplant recipient register who were taking empagliflozin or a combination of empagliflozin and metformin were included. Consequently, their safety and efficacy parameters were examined.
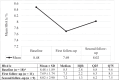
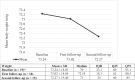
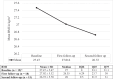
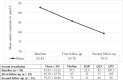
Results: A total of 20 patients were included in this study. There was an improvement in haemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) levels, body weight and stability in serum creatinine. Additionally, there was no increased risk of genitourinary infections, hypoglycaemia or diabetic ketoacidosis.
Conclusions: Although larger studies are needed to examine the use of empagliflozin in cardiac transplant patients, this small study provides assurance that empagliflozin is safe for use in cardiac transplant recipients.
Keywords: Empagliflozin; SGLT2 Inhibitors; Saudi Arabia; Type 2 Diabetes.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on cardiovascular events, death, and major safety outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016 May;4(5):411-9. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)00052-8. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27009625
-
Use of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in solid organ transplant recipients with pre-existing type 2 or post-transplantation diabetes mellitus: A systematic review.Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2023 Jan;37(1):100729. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2022.100729. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2023. PMID: 36427372
-
Glucose-lowering agents for treating pre-existing and new-onset diabetes in kidney transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 27;2(2):CD009966. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009966.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 30;8:CD009966. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009966.pub3. PMID: 28238223 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Insulin and glucose-lowering agents for treating people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 24;9(9):CD011798. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011798.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30246878 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Empagliflozin on Sarcopenia Risk, Body Composition, and Muscle Strength in Type 2 Diabetes: A 24-Week Real-World Observational Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jun 26;61(7):1152. doi: 10.3390/medicina61071152. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40731782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fonseca-Correa JI, Correa-Rotter R. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors mechanisms of action: A review. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021; 8:777861. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.777861. 10.3389/fmed.2021.777861 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015; 373:2117–28. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1504720. 10.1056/NEJMoa1504720 - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med 2020; 383:1413–24. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2022190. 10.1056/NEJMoa2022190 - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Ferreira JP, Bocchi E, Böhm M, et al. Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med 2021; 385:1451–61. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2107038. 10.1056/NEJMoa2107038 - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- McGuire DK, Shih WJ, Cosentino F, Charbonnel B, Cherney DZI, Dagogo-Jack S, et al. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol 2021; 6:148–58. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2020.4511. 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.4511 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
