Glioma-Associated Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Derived Exosomal miR-191 Promotes the Proneural-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Glioblastoma Cells via PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling
- PMID: 40657483
- PMCID: PMC12248735
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S515771
Glioma-Associated Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Derived Exosomal miR-191 Promotes the Proneural-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Glioblastoma Cells via PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling
Abstract
Background: The proneural-to-mesenchymal transition (PMT) represents a crucial phenotypic transformation in glioblastoma. Glioma-associated mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (GaMSCs) play a significant role in diverse biological processes of gliomas. However, the impact of exosomes released from GaMSCs (GaMSCs-Exos) on the PMT of glioblastoma remains inadequately understood. This study aimed to explore the effects and mechanisms of GaMSCs-derived exosomal miRNA-191-5p on the PMT of glioblastoma.
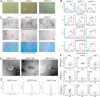
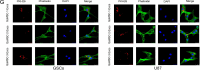
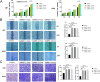
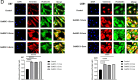
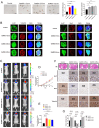
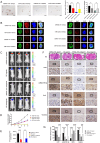
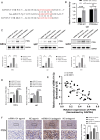
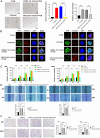
Methods and results: Conditioned medium from three independently established GaMSCs lines (GaMSCs-CM) significantly enhanced the tumorigenicity of glioma cells. Further analysis demonstrated that GaMSC-Exos, isolated from GaMSCs-CM, promoted both the tumorigenicity and PMT of glioma cells, both in vitro and in vivo. Exosomal miR-191-5p derived from GaMSCs was identified as the principal mediator. Overexpression and inhibition of miR-191-5p affected the tumorigenicity and PMT of glioma cells, in both laboratory and animal models. Bioinformatics analyses and luciferase reporter assays confirmed that miR-191-5p targets PTEN. Additionally, rescue experiments indicated that increased PTEN expression could reverse the effects of miR-191-5p overexpression on tumorigenicity and PMT through modulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the role of GaMSC-Exos in mediating the intercellular transfer of miRNA-191-5p, which facilitates the PMT of glioma. The process underlying the enhanced aggressiveness and PMT is driven by miR-191-5p, promoting glioma progression by targeting PTEN and activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Keywords: exosomes; glioma-associated mesenchymal stromal/stem cells; miR-191-5p; proneural to mesenchymal transition.
© 2025 Lv et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exosomal miR-21-5p from glioma associated mesenchymal stem cells promotes the progression and glycolysis of glioblastoma via PDHA1.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 17;15(1):2320. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86580-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39833311 Free PMC article.
-
Rab27a+CAF exosomal miR-9-5p promotes osteosarcoma progression via CREBRF/MAPK signaling pathway.Cell Signal. 2025 Oct;134:111964. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111964. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40581265
-
CAF-derived exosomal miR-196b-5p after androgen deprivation therapy promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells through HOXC8/NF-κB signaling pathway.Biol Direct. 2025 Jul 4;20(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13062-025-00667-2. Biol Direct. 2025. PMID: 40615904 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of valid endogenous control genes for determining gene expression in C6 glioma cell line treated with conditioned medium from adipose-derived stem cell.Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 Oct;75:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.08.035. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 26463634
-
Emerging Insights into the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway and Non-Coding RNA-mediated Drug Resistance in Glioblastoma.Curr Mol Med. 2025;25(6):710-722. doi: 10.2174/0115665240309647240516042716. Curr Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 38840404 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

