Analysis of treatment planning time and optimization parameters for inverse planning for intracavitary and interstitial brachytherapy in uterine cervical cancer
- PMID: 40657692
- PMCID: PMC12257335
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.70157
Analysis of treatment planning time and optimization parameters for inverse planning for intracavitary and interstitial brachytherapy in uterine cervical cancer
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the effect of inverse planning parameters on dose-volume indices in brachytherapy for uterine cervical cancer.
Methods: Fourteen consecutive patients with cervical cancer who received intracavitary and interstitial brachytherapy (IC/ISBT) were selected. Tandem, ovoid, and interstitial needles were used in all cases. The evaluation plans were recalculated from the first fraction of clinical brachytherapy plans. The correlation between the 11 dose optimization parameters of inverse planning and the 13 dose-volume indices was evaluated. The parameters were adjusted in five levels, and dose optimization was performed in hybrid inverse planning optimization (HIPO). Spearman's rank correlation and multiple regression analyses were conducted to assess the association between the parameters and the indices. The indices included clinical target volume (CTV) dose, organ-at-risk (OAR) dose, homogeneity, and conformity. Additionally, the correlation between optimization parameters and calculation time was investigated, along with a technique for efficiently generating treatment plans.
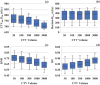
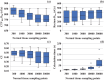
Results: "CTV Max Weight" and "OAR Max Weight" were the key parameters significantly affecting the indices. Increasing "CTV Max Weight" improved homogeneity but reduced the target coverage. The effect of "OAR Max Weight" on the dose reduction of CTVHR D90 (β = -0.59) was more significant than that on the dose reduction of OAR D2cc (β = -0.21). In addition, adjusting "CTV Min Weight" and "CTV Volume" could reduce the hyper-dose sleeve without increasing the OAR dose. A large number of normal tissue sampling points could negatively affect the dose distributions and increase the calculation times.
Conclusion: "CTV Max Weight" and "OAR Max Weight" were the most influential parameters in HIPO, significantly affecting dose-volume indices in IC/ISBT for uterine cervical cancer. Additionally, parameters that regulate the hyper-dose sleeve and needle-delivered dose were identified. The quality of treatment planning can be maintained and planning time reduced by appropriately optimizing these parameters.
Keywords: HIPO; IC/ISBT; brachytherapy; cervical cancer; inverse planning; optimization.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of The American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Karabis A, Giannouli S, Baltas D. 40 HIPO: a hybrid inverse treatment planning optimization algorithm in HDR brachytherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2005;76:S29. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(05)81018-7 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

